https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-025-01009-7
Regular Article - Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Singly differential cross section in the generalized binary-encounter-Bethe model for electron impact ionization of polyatomic molecules
1
College of Physical Science and Technology, Shenyang Normal University, 110034, Shenyang, People’s Republic of China
2
College of Science, Shenyang Aerospace University, 110136, Shenyang, People’s Republic of China
3
College of Physics, Jilin University, 130012, Changchun, People’s Republic of China
4
Helmholtz-Institut Jena, D-07743, Jena, Germany
5
GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH, D-64291, Darmstadt, Germany
6
Theoretisch-Physikalisches Institut, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, 07743, Jena, Germany
Received:
28
February
2025
Accepted:
10
May
2025
Published online:
11
June
2025
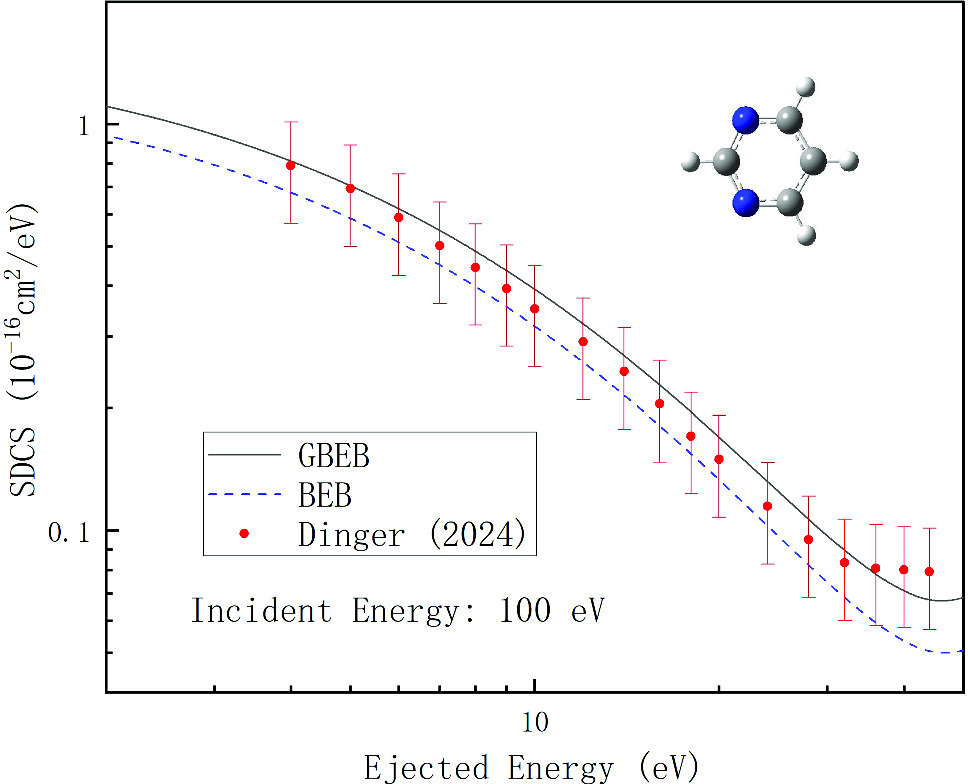
We assess the effectiveness of singly differential cross sections (SDCS) for electron impact ionization of water and pyrimidine molecules by applying the generalized binary-encounter-Bethe (GBEB) model. When compared to the original binary-encounter-Bethe (BEB) model, the GBEB model is developed based on corrected acceleration energies [Y.-C. Wang et al., Phys. Rev. A 109, 022804 (2024)]. The SDCS calculated by the GBEB model shows improved agreement with the experimental data compared to the BEB predictions. The agreement becomes better as the energy of the ejected electron increases. For low incident energies, the acceleration correction of the GBEB model improves the SDCS at low incident energies.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.