https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-025-01012-y
Regular Article - Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Electron and positron scattering by water molecules: cross sections and transport characteristics
1
Department of Physics, University of Rajshahi, 6205, Rajshahi, Rajshahi, Bangladesh
2
Department of Physics, Dagestan State University, 367000, Makhachkala, Dagestan, Russia
3
Department of Physics, Pabna University of Science and Technology, 6600, Pabna, Rajshahi, Bangladesh
4
Division of Radiation Protection and Safety Control, Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center, Tohoku University, 980-8578, 6-3 Aoba, Aramaki, Aoba, Sendai, Japan
Received:
6
April
2025
Accepted:
16
May
2025
Published online:
9
June
2025
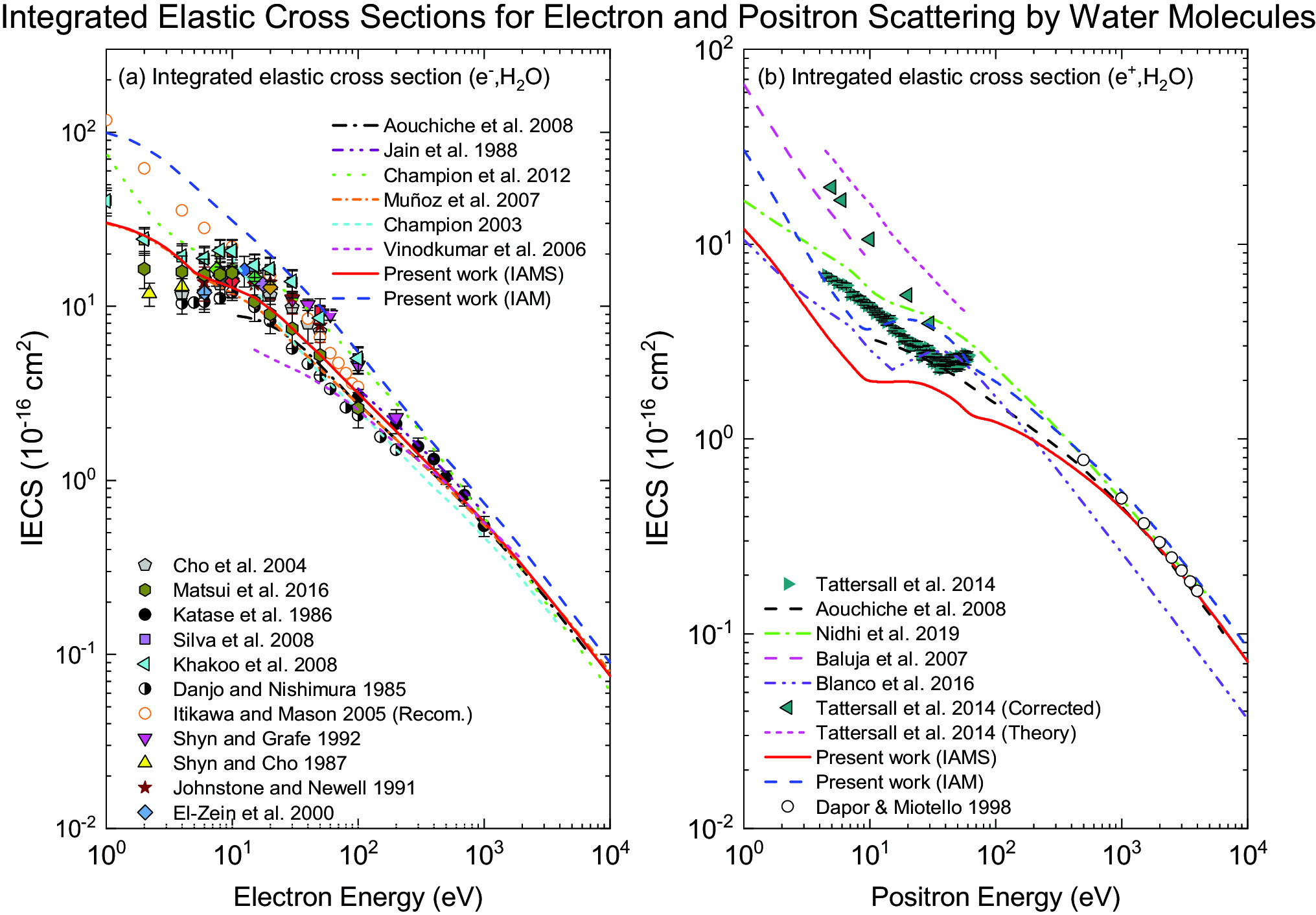
A theoretical calculation on the elastic and inelastic scattering of electrons and positrons in water molecule is performed for incident energies ranging from 1 eV - 10 keV. Dirac relativistic partial-wave method with a complex optical potential for free-atoms is adopted. Various scattering observables are obtained by taking into account the geometrical screening corrections due to partial overlapping of constituent atoms, as seen by the incident projectiles in the coherent sum of scattering amplitudes. Furthermore, the Monte Carlo method is used to calculate the transport characteristics of electrons in H O vapor for electric field E/N = 1-300 Td, taking into account inelastic collisions. The drift velocity, average electron energy, ionization coefficient and mobility coefficients are calculated. Admixtures of 2% and 10% water to argon are found to produce negative differential conductivity (NDC), despite NDC being absent from the pure gases. The results obtained are compared to the existing experimental data and theoretical calculations and a reasonable agreement is observed.
O vapor for electric field E/N = 1-300 Td, taking into account inelastic collisions. The drift velocity, average electron energy, ionization coefficient and mobility coefficients are calculated. Admixtures of 2% and 10% water to argon are found to produce negative differential conductivity (NDC), despite NDC being absent from the pure gases. The results obtained are compared to the existing experimental data and theoretical calculations and a reasonable agreement is observed.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.