https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-025-01010-0
Regular Article - Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Calculations of M-shell X-ray production cross sections for Ho induced by 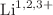 ions
ions
Key Laboratory of Atomic and Molecular Physics & Functional Materials of Gansu Province, College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Northwest Normal University, 730070, Lanzhou, China
a
xiely@nwnu.edu.cn
b
dongcz@nwnu.edu.cn
Received:
22
March
2025
Accepted:
12
May
2025
Published online:
23
May
2025
The total M-shell and 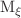 ,
, 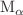 ,
, 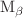 and
and 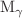 X-ray production cross sections of Ho induced by 1 - 9 MeV
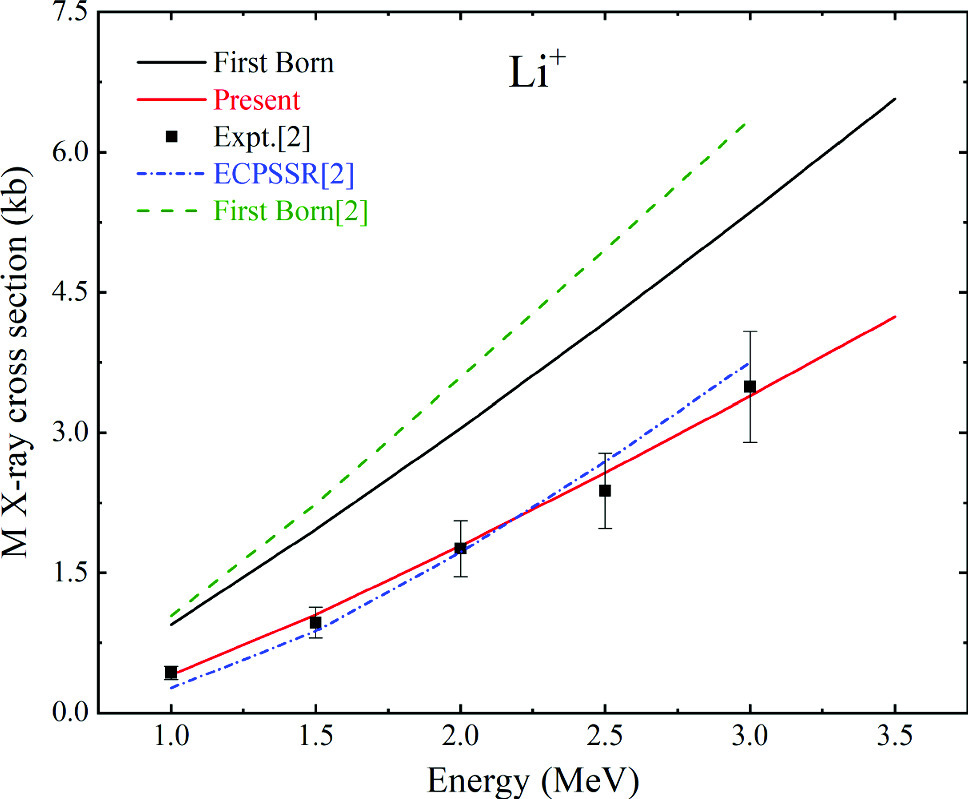
X-ray production cross sections of Ho induced by 1 - 9 MeV 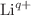 (q = 1 - 3) ions are calculated using the atomic electron removal cross sections code based on the ECPSSR theory, which includes energy loss and Coulomb deflection effects, perturbed stationary state approximation with relativistic correction, for direct ionization and non-radiative electron capture. The effects of projectile energy loss and Coulomb deflection of the projectile, perturbation of electron’s stationary state and relativistic correction of the target electron, as well as electron capture to the higher shells of the projectile are determined, by making a comprehensive study of the projectile energy and charge state dependence of the M-shell X-ray production cross sections for targets. The calculations show excellent agreement with the available experimental values. It is found that the various M series lines, that is,
(q = 1 - 3) ions are calculated using the atomic electron removal cross sections code based on the ECPSSR theory, which includes energy loss and Coulomb deflection effects, perturbed stationary state approximation with relativistic correction, for direct ionization and non-radiative electron capture. The effects of projectile energy loss and Coulomb deflection of the projectile, perturbation of electron’s stationary state and relativistic correction of the target electron, as well as electron capture to the higher shells of the projectile are determined, by making a comprehensive study of the projectile energy and charge state dependence of the M-shell X-ray production cross sections for targets. The calculations show excellent agreement with the available experimental values. It is found that the various M series lines, that is, 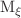 ,
, 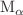 ,
, 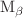 and
and 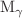 X-ray production cross sections, are sensitive to the charge state and energy of the incident Li ions, while the intensity ratios,
X-ray production cross sections, are sensitive to the charge state and energy of the incident Li ions, while the intensity ratios, 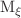 /
/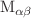 and
and 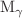 /
/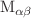 , do not exhibit a strong dependence on the projectile charge state.
, do not exhibit a strong dependence on the projectile charge state.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.