https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-025-01006-w
Regular Article – Clusters and Nanostructures
Generation and optimization of gold nanoclusters via reinforcement learning
1
State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing, Northwestern Polytechnical University, 710072, Xi’an, China
2
School of Material Science and Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, 710072, Xi’an, China
Received:
28
January
2025
Accepted:
24
April
2025
Published online:
25
May
2025
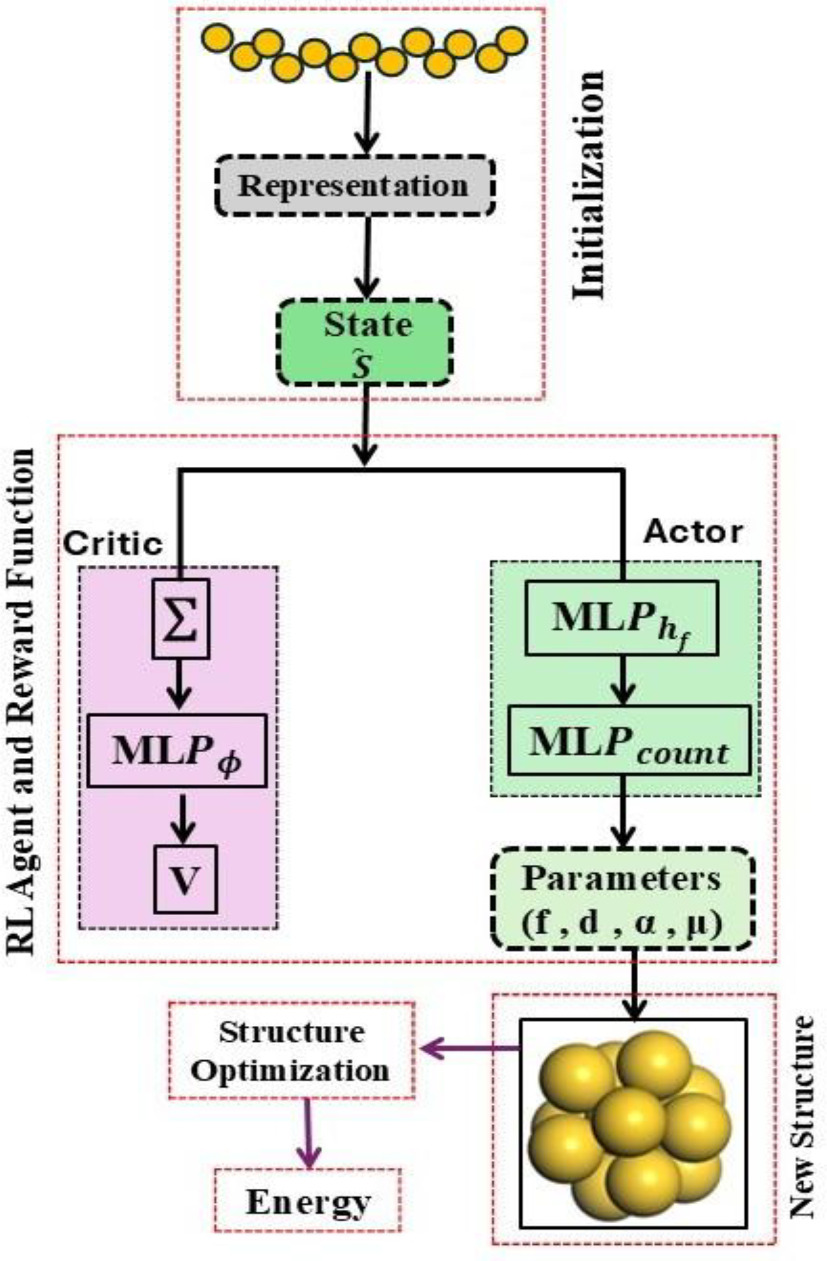
The identification and prediction of atomic cluster structures are crucial in nanocluster and materials research, as the molecular structure significantly influences the properties of nanoclusters. This study presents an innovative approach for generating and optimizing gold Au13, Au7, Au6, and Au5 nanoclusters using reinforcement learning (RL). Conventional techniques for optimizing nanoparticle structures are significantly expensive in computation and have some restrictions when exploring a broad range of design possibilities. To overcome these challenges, we used a policy-based RL model that learns how to arrange atoms on a canvas to minimize the potential energy of the nanocluster, like an actor–critic model. The agent works under a reward function based on the molecule’s energy, systematically positioning atoms on a canvas until it reaches convergence. The performance and evaluation of our RL model are assessed by local optimization techniques, specifically the BFGS optimization algorithm and simulated annealing. We conclude that the RL method is effective for identifying the configuration of Au13 nanoparticles and achieving a stable and low-energy icosahedral structure. The complexity of the energy landscape of nanoalloys renders the determination of their structure a complicated task. This study points out the potential of reinforcement learning in materials science for designing and optimizing nanoparticles with stability characteristics.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.