https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00902-x
Regular Article – Optical Phenomena and Photonics
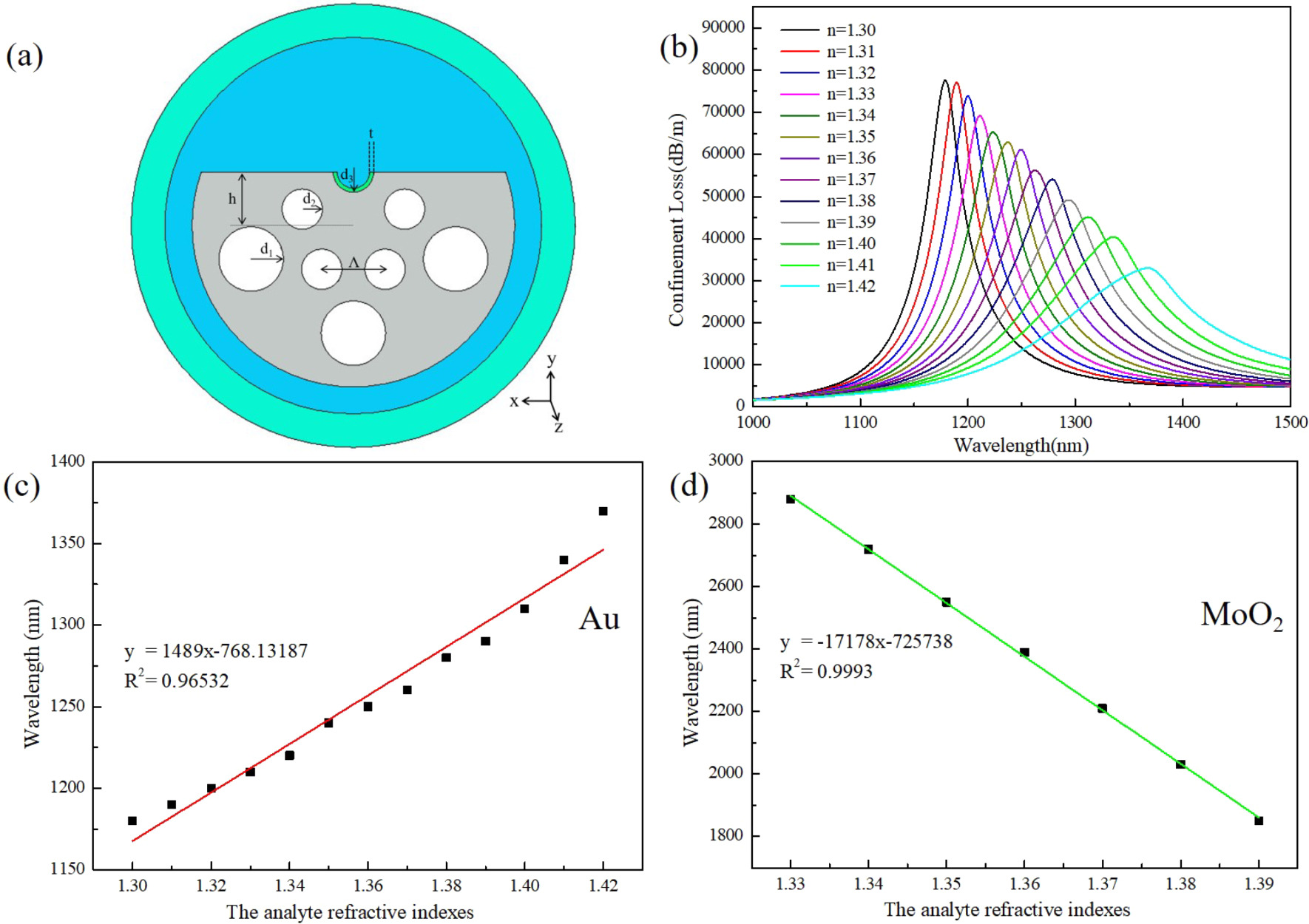
Ultra-wide measurement range D-shaped photonic crystal fiber sensor based on surface plasmon resonance
1
Xinjiang Institute of Engineering, 830091, Urumqi, China
2
College of Physics and Electronic Science, Shanxi Datong University, 037009, Datong, China
3
Key Laboratory of New Energy and Materials Research, Xinjiang Institute of Engineering, 830023, Urumqi, China
b
dtdxyangying@163.com
c
dongjiyu2814@163.com
Received:
23
February
2024
Accepted:
3
August
2024
Published online:
31
August
2024
In this paper, a kind of D-type photonic crystal fiber (PCF) sensor with an ultra-wide detection range based on micro-opening gold film coating is proposed. This sensor allows for the sensing detection of the refractive index (RI) of the analyte ranging from 1.30 to 1.42. However, the sensor coated with a micro-opening gold film only achieves an average wavelength sensitivity of 1489 nm/RIU in the x-polarization direction. To improve the performance of the sensor, an attempt was made to replace the micro-opening gold film with MoO2 nanofilm. After simulation calculation, it was found that the RI detection range of the sensor using MoO2 nanofilm became 1.33–1.39. Excitingly, the average wavelength sensitivity in the x-polarized direction reaches 17, 178 nm/RIU, which is 11.5 times better than the original sensor. This implies that the sensor is more sensitive to changes in the RI and can provide more accurate sensing and detection results. It has been demonstrated that the performance of a D-type PCF sensor can be significantly improved by using MoO2 nanofilm. This improvement helps to expand the application domain of sensors and enhance the accuracy of sensing detection. We believe that this research result has important implications for the development of fiber sensor technologies.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.