https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00871-1
Regular Article - Atomic and Molecular Collisions
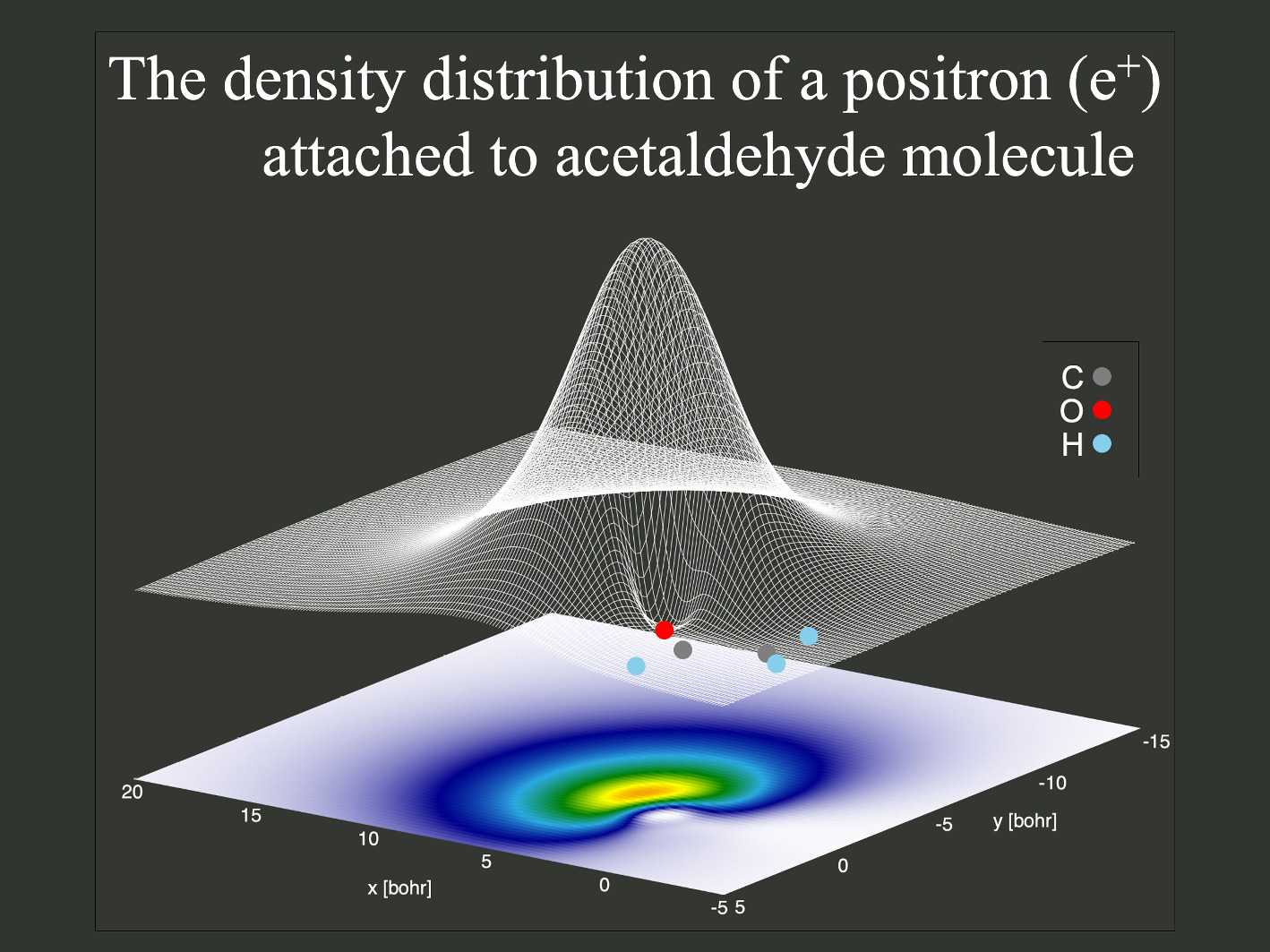
Theoretical analysis of H/D isotope effect on the binding of a positron to acetaldehyde molecule
Quantum Chemistry Division, Yokohama City University, Seto 22-2, Kanazawa-Ku, 236-0027, Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan
b
tachi@yokohama-cu.ac.jp
c
ykita@yokohama-cu.ac.jp
Received:
2
October
2023
Accepted:
30
May
2024
Published online:
28
August
2024
We theoretically analyzed positron affinities (PAs) of acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) and its deuterated (CD3CDO) molecules at vibrational excited states with multi-component molecular orbital and vibrational quantum Monte Carlo methods. In the fundamental tone states, the PA value at the C=O stretching vibrational mode of acetaldehyde becomes increased by 9.8 meV (+ 12%) from the vibrational ground state of 84.5 meV, while that at the C-H (aldehyde group) stretching vibrational mode decreased by 2.8 meV ( 3%). We also confirmed that each vibrational state has a different H/D isotope shift in PA values. Such non-uniformity in quantum vibrational influence on PA values and its H/D isotope shifts dominantly arise from the change in dipole moment by vibrational excitations.
3%). We also confirmed that each vibrational state has a different H/D isotope shift in PA values. Such non-uniformity in quantum vibrational influence on PA values and its H/D isotope shifts dominantly arise from the change in dipole moment by vibrational excitations.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.