https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00877-9
Regular Article
In-situ deposition of silver nanoparticles onto glass by non-thermal plasma jet
1
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Vali-E-Asr University of Rafsanjan, Rafsanjan, Iran
2
Plasma and Nuclear Fusion Research School, Nuclear Science and Technology Research Institute (NSTRI), Box 14155-1339, Tehran, Iran
Received:
8
November
2023
Accepted:
7
June
2024
Published online:
2
July
2024
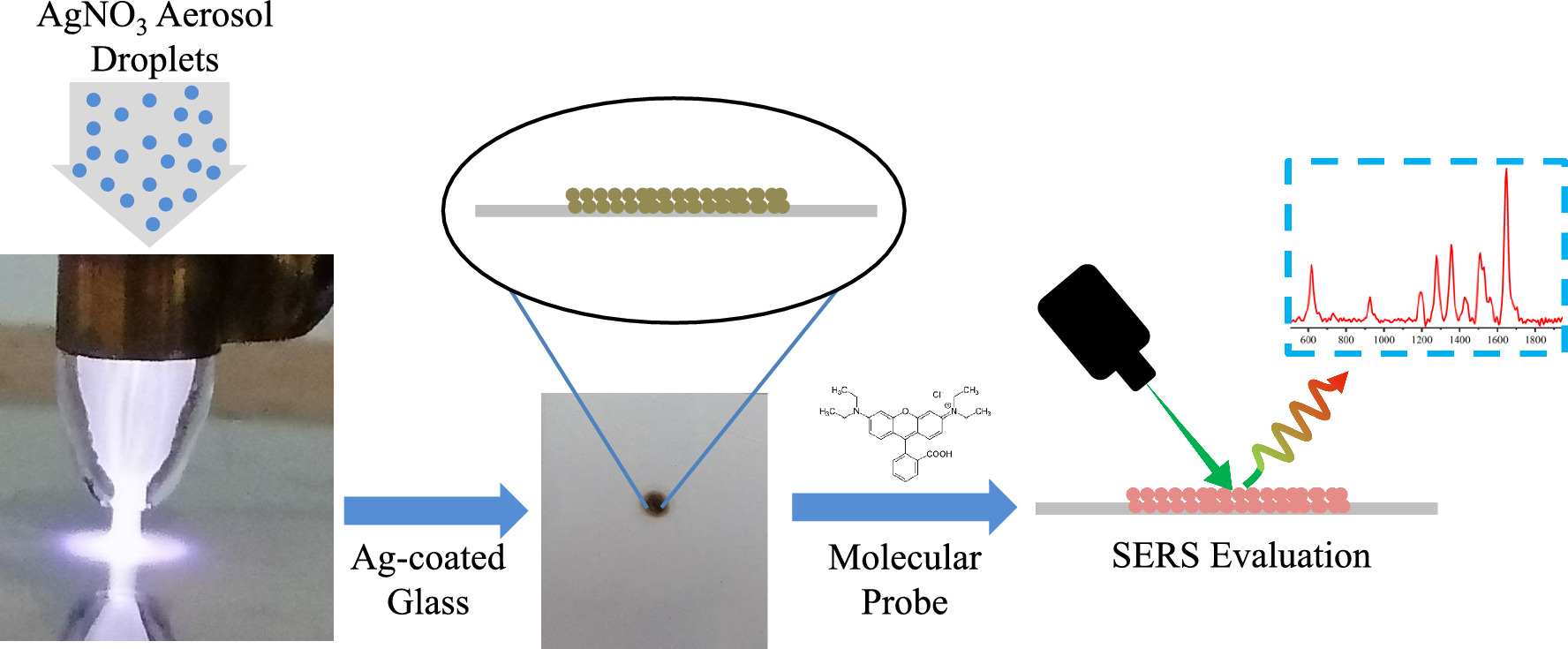
In this study, we employed an atmospheric-pressure non-thermal plasma jet that used silver nitrate solution as the precursor which is injected, in an aerosol state, into the plasma jet to create silver nanoparticles with the desired distribution on the glass substrate. The crystal structure and morphology of the Ag nanoparticles printed on the glass substrate were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), the field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), and the atomic force microscope (AFM). The XRD patterns confirm Ag nanostructure deposition on the glass. FESEM results show that Ag nanoparticles’ are almost spherical in shape and by increasing the applied voltages, the Ag nanoparticles' size and density increases, and AFM images confirm the results of FESEM images. Rhodamine B with various concentrations was employed to determine the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) performance of Ag nanoparticles printed on the glass. It shows high sensitivity for Ag layers created by plasma to a threshold that even for the lower concentrations of 10−10M, Rhodamine B is still detectable. There was the optimum SERS effect at a 7 kV voltage. Also, the plasma-printed Ag layers are able to detect methylene blue, usually used as a fungicide in fish ponds and aquariums, even in low concentrations of 10−9M. The residual sulfur dioxide (SO2) of raisins was detected using a plasma-printed silver layer. This shows the application of this plasma-printed silver layer for residual SO2 detection in the food industry.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00877-9.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.