https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00684-8
Regular Article – Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Angular distribution of the characteristic line  of thallium ions: hyperfine-induced multipole interference
of thallium ions: hyperfine-induced multipole interference
1
Key Laboratory of Atomic and Molecular Physics and Functional Materials of Gansu Province, College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Northwest Normal University, 730070, Lanzhou, People’s Republic of China
2
Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Fröbelstieg 3, 07743, Jena, Germany
3
GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH, Planckstrasse 1, 64291, Darmstadt, Germany
4
Theoretisch-Physikalisches Institut, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Max-Wien-Platz 1, 07743, Jena, Germany
Received:
4
April
2023
Accepted:
24
May
2023
Published online:
5
June
2023
Within the framework of the density matrix theory, the angular distribution of the characteristic magnetic-quadrupole line  following electron-impact excitation of heliumlike thallium ions with nuclear spin
following electron-impact excitation of heliumlike thallium ions with nuclear spin 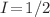 has been investigated by using the multiconfigurational Dirac–Hartree–Fock method and the relativistic distorted-wave theory. Special attention has been paid to exploring the question of how the angular distribution of the characteristic line is affected by the multipole interference between the dominant magnetic-quadrupole and hyperfine-induced electric-dipole decay channels of its hyperfine-structure-resolved component
has been investigated by using the multiconfigurational Dirac–Hartree–Fock method and the relativistic distorted-wave theory. Special attention has been paid to exploring the question of how the angular distribution of the characteristic line is affected by the multipole interference between the dominant magnetic-quadrupole and hyperfine-induced electric-dipole decay channels of its hyperfine-structure-resolved component 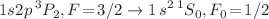 . To this aim, detailed calculations are performed for spin-1/2
. To this aim, detailed calculations are performed for spin-1/2  Tl
Tl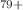 and
and 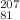 Tl
Tl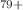 ions with (relatively) large nuclear magnetic dipole moment. It is found that the hyperfine-induced multipole interference contributes to making the angular distribution of the magnetic-quadrupole line
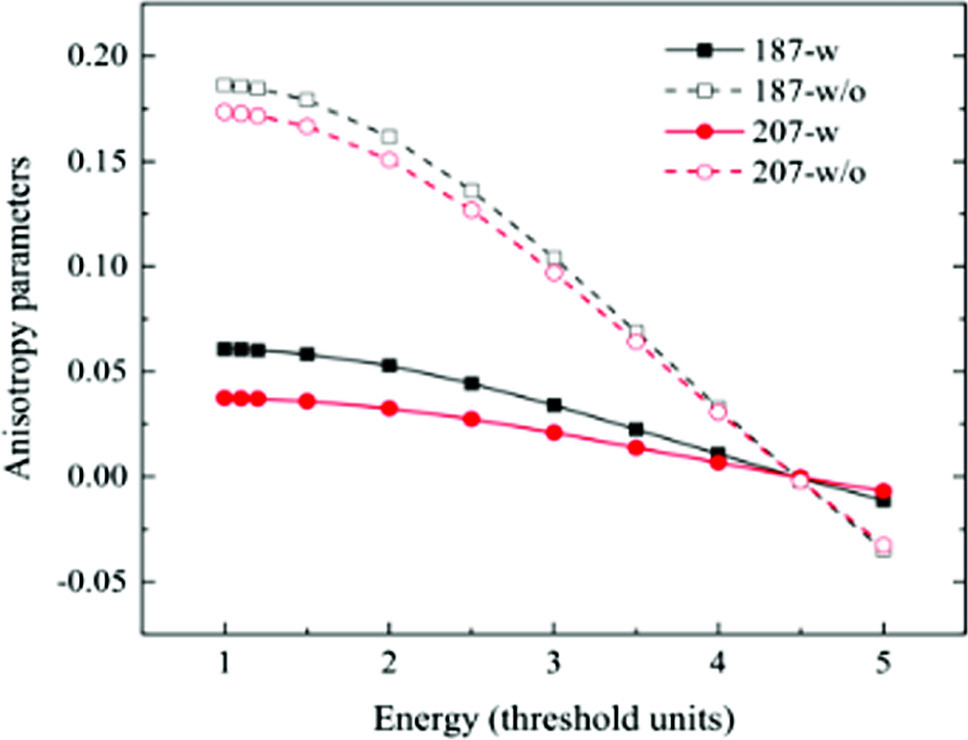
ions with (relatively) large nuclear magnetic dipole moment. It is found that the hyperfine-induced multipole interference contributes to making the angular distribution of the magnetic-quadrupole line  less anisotropic for all the impact electron energies considered, although at any given impact energy its angular emission pattern remains always qualitatively consistent with each other for both the two cases without and with the interference contribution included. Moreover, for the case with the interference considered the angular distribution of the magnetic-quadrupole line is found to be sensitive to the nuclear magnetic dipole moment of the spin-1/2 ions, especially at low impact electron energies.
less anisotropic for all the impact electron energies considered, although at any given impact energy its angular emission pattern remains always qualitatively consistent with each other for both the two cases without and with the interference contribution included. Moreover, for the case with the interference considered the angular distribution of the magnetic-quadrupole line is found to be sensitive to the nuclear magnetic dipole moment of the spin-1/2 ions, especially at low impact electron energies.
Atomic and Molecular Data and Their Applications: ICAMDATA 2022. Guest editors: Annarita Laricchiuta, Iouli E. Gordon, Christian Hill, Gianpiero Colonna, Sylwia Ptasinska.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.