https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00173-w
Regular Article - Molecular Physics and Chemical Physics
Structure and collision-induced dissociation of the protonated cyclo His-Phe dipeptide: mechanistic studies and stereochemical effects
1
CNRS, Institut des Sciences Moléculaires d’Orsay, Université Paris-Saclay, 91405, Orsay, France
2
Laboratoire de Chimie Théorique, Sorbonne Université UMR 7616 CNRS, 4, Place Jussieu, 75005, Paris, France
f
anne.zehnacker-rentien@universite-paris-saclay.fr
Received:
22
November
2020
Accepted:
6
May
2021
Published online:
31
May
2021
The role of stereochemical factors on the structure and the fragmentation paths of the protonated cyclic dipeptide cyclo histidine–phenylalanine is studied under ion traps conditions by combining tandem mass spectrometry, laser spectroscopy, quantum chemical calculations and chemical dynamics simulations. Vibrational spectroscopy obtained by Infrared Multiple Photon Dissociation (IRMPD) reveals a small difference between the two diastereomers, c- and c-
and c-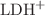 , arising mainly from ancillary CH...
, arising mainly from ancillary CH... interactions. In contrast, there is a strong influence of the residues chirality on the collision-induced dissociation (CID) processes. Chemical dynamics simulations rationalize this effect and evidence that proton mobility takes place, allowing isomerization to intermediate cyclic structures that are different for c-
interactions. In contrast, there is a strong influence of the residues chirality on the collision-induced dissociation (CID) processes. Chemical dynamics simulations rationalize this effect and evidence that proton mobility takes place, allowing isomerization to intermediate cyclic structures that are different for c- and c-
and c-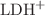 , resulting in different barriers to proton mobility. This effect is related to the protonation of the imidazole ring. It contrasts with the minute stereochemical effects observed for other cyclic dipeptides in which the proton is borne by an amide CO.
, resulting in different barriers to proton mobility. This effect is related to the protonation of the imidazole ring. It contrasts with the minute stereochemical effects observed for other cyclic dipeptides in which the proton is borne by an amide CO.
Supplementary Information The online version of this article (https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00173-w) contains supplementary information, which is available to authorized users.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




