https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00047-1
Regular Article - Topical Issue
Confinement of an ultra-cold-matter wave packet near the delocalization threshold by a waveguide bend with two or more contact impurities
1 Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Av. Universidad 3000, Circuito Exterior S/N Delegación Coyoacán, C.P. 04510, Ciudad Universitaria, Mexico City, Mexico
2 Instituto de Ciencias Físicas, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Av. Universidad S/N, 62210, Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico
Received:
14
December
2020
Accepted:
9
January
2021
Published online: 1 February 2021
The properties of confined quantum systems are of fundamental importance in the understanding of quantum behavior at extreme conditions. One of such quantum systems at extreme conditions is an ultra-cold quantum matter wave packet confined by a square well potential. The square well potential could be produced by a bend in a waveguide in an atom chip. Of further interest is the presence of contact impurities inside the bend produced by guide defects. In order to study such a system, its properties are well described by the nonlinear Schrödinger equation. In this work, we generalize our previous work (Méndez-Fragoso and Cabrera-Trujillo in Eur J Phys D 69:139, 2015) to study the ground state behavior of a quantum matter wave packet under confinement by a bend modeled by an attractive square well potential of strength 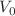 and width 2R in the presence of several contact impurities represented by delta potentials with strength
and width 2R in the presence of several contact impurities represented by delta potentials with strength 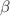 placed inside it at the threshold of delocalization, i.e., at the point where the well has trapped the maximum number of particles. We find that the maximum number of atoms held by the squared well potential only depends on the total strength of the contact impurities and not on their position. This implies that the maximum number of trapped particles is the same for one or more contact impurities as long as the combined strength is the same. For small
placed inside it at the threshold of delocalization, i.e., at the point where the well has trapped the maximum number of particles. We find that the maximum number of atoms held by the squared well potential only depends on the total strength of the contact impurities and not on their position. This implies that the maximum number of trapped particles is the same for one or more contact impurities as long as the combined strength is the same. For small 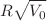 values of the squared well potential, the number of particles trapped at the delocalization threshold is lower than when no contact impurities are present and decreases more as the contact impurity repulsive strength increases. This induces a threshold on the maximum number of particles trapped by an attractive squared well at
values of the squared well potential, the number of particles trapped at the delocalization threshold is lower than when no contact impurities are present and decreases more as the contact impurity repulsive strength increases. This induces a threshold on the maximum number of particles trapped by an attractive squared well at 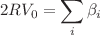 . The matter wave packet profile shows the effect of the contact impurity as a wedge shape at the contact impurity position.
. The matter wave packet profile shows the effect of the contact impurity as a wedge shape at the contact impurity position.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




