https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-020-00018-y
Regular Article - Topical Issue
Interaction between iron ion and dipole carbon monoxide inside spherical cavities
1
Department of Physics, Institute of Biosciences, Humanities and Exact Sciences (Ibilce), Sao Paulo State University (Unesp), Campus Sao Jose do Rio Preto, Sao Jose do Rio Preto, 15054-000, São Paulo, Brazil
2
Federal Institute of Sao Paulo, Campus Votuporanga, Votuporanga, 15503-110, São Paulo, Brazil
Received:
31
July
2020
Accepted:
3
November
2020
Published online:
21
January
2021
The interactions that occur within hemeproteins are important for biological systems and they are of interest for understanding living systems. In this way, it is important to know the vibrational and electrostatic interactions in this system. In this article, a study is made using a new approach to describe the interaction between iron ions and carbon monoxide inside spherical cavities that mimic volumes of protein cavities in three different media (vacuum, water and ice). We use an alternative trial wavefunction as an ansatz in the Variational Method for the calculation of the energy for a confined ion–dipole system. This trial function is inspired by Supersymmetric Quantum Mechanics. One of the results obtained is the value of the ground state energy of this interaction in a vacuum inside a spherical cavity of radius approximately equal to 12 Bohr radius obtained by the Variational Method. This result is compared with the energy value obtained by the second order Moller–Plesset perturbative method and there is a difference of approximately 1.9 10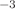 hartree (3.87
hartree (3.87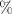 ).
).
Guest editors: C.N. Ramachandran, Vincenzo Aquilanti, Henry Ed Montgomery and N. Sathyamurthy.
© EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021





