https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2008-00265-1
The structure and stability of Si@Al12Hn (n=1-14) clusters
1
School of Physics and Material Science, Anhui University, 230039 Hefei, Anhui, P.R. China
2
Department of Chemistry, the University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, 85721, USA
3
National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures and Department of Physics, Nanjing University, 210093 Nanjing, Jiangsu, P.R. China
Corresponding author: a qllufd@vip.sina.com
Received:
13
August
2008
Published online:
20
December
2008
Density functional theory has been employed in order to investigate the
structure and stability of Si@Al12Hn (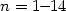 ) clusters.
Hydrogenated Si@Al12 clusters exhibit pronounced stability for even
numbers of H atoms. Large binding energy, HOMO-LUMO gaps and increased
ionization potentials imply that these clusters should be physically and
chemically stable. The analysis of the charge density of the HOMO plot
illustrates that a pair of hydrogen atoms prefer to occupy opposing on-top
sites for clusters with an even n number. Studies of deformation charge
density plots demonstrate that significant charge transfer occurs from the
Si@Al12 to the H atoms.
) clusters.
Hydrogenated Si@Al12 clusters exhibit pronounced stability for even
numbers of H atoms. Large binding energy, HOMO-LUMO gaps and increased
ionization potentials imply that these clusters should be physically and
chemically stable. The analysis of the charge density of the HOMO plot
illustrates that a pair of hydrogen atoms prefer to occupy opposing on-top
sites for clusters with an even n number. Studies of deformation charge
density plots demonstrate that significant charge transfer occurs from the
Si@Al12 to the H atoms.
PACS: 36.40.Cg – Electronic and magnetic properties of clusters / 36.40.Qv – Stability and fragmentation of clusters / 73.22.-f – Electronic structure of nanoscale materials: clusters, nanoparticles, nanotubes, and nanocrystals / 82.33.Hk – Reactions on clusters
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2009




