https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-025-01014-w
Regular Article - Plasma Physics
Arbitrary amplitude dust ion acoustic soliton in dusty plasmas with regularized kappa distributed electrons
School of Physics and Technology, Nantong University, Seyuan Road, 226019, Nantong, Jiangsu, China
Received:
11
June
2024
Accepted:
29
October
2024
Published online:
28
July
2025
Arbitrary amplitude dust ion acoustic solitons (DIASs) in plasma consisting of positive ions, regularized kappa distributed electrons and negatively charged dust grains have been investigated by the Sagdeev pseudopotential method. It is found that negative DIASs exist only in a certain range of spectral index  and cutoff parameter
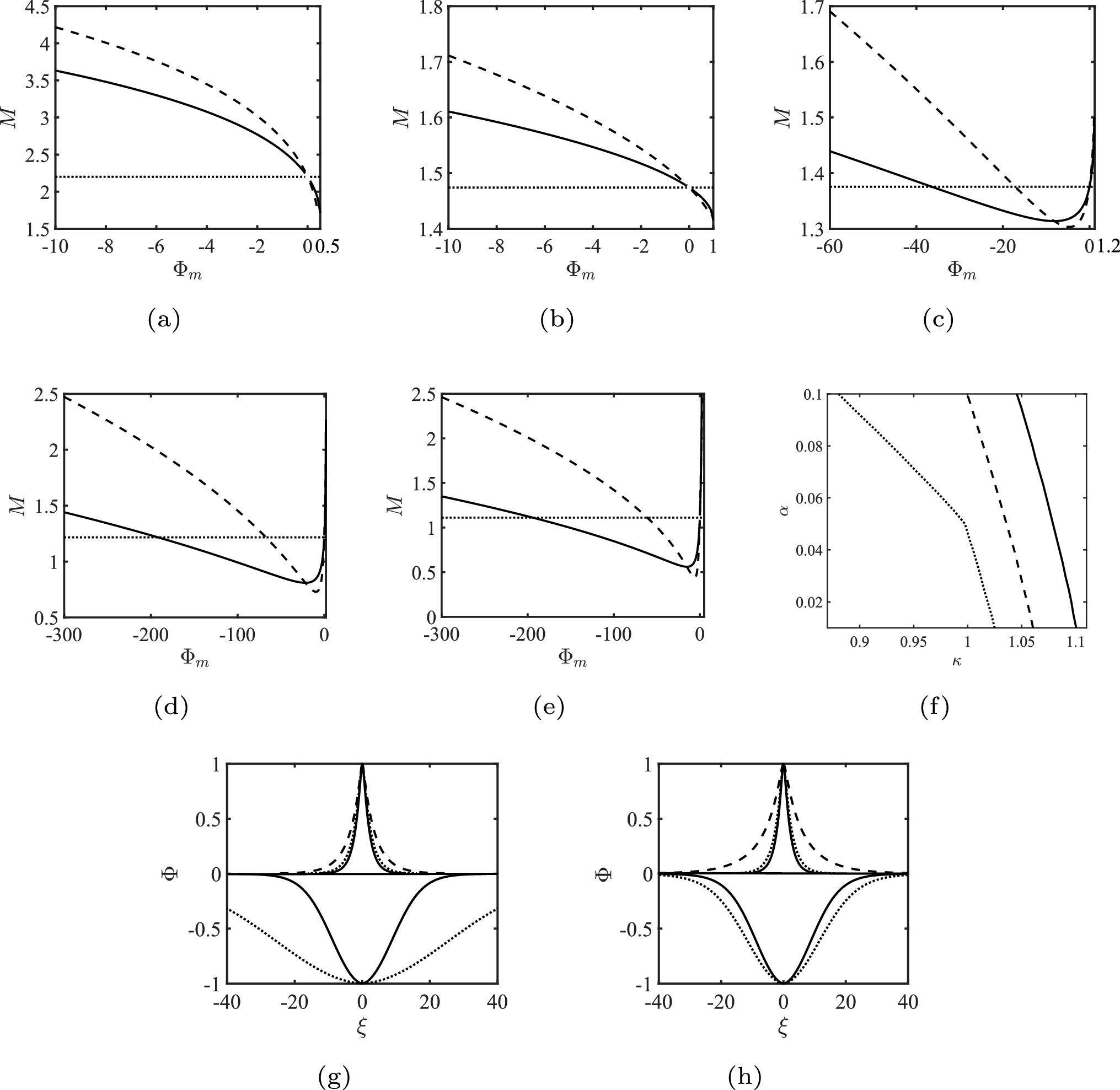
and cutoff parameter 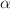 , which increases with the electron concentration. Correspondingly, the region of
, which increases with the electron concentration. Correspondingly, the region of  and
and 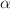 for the coexistence of negative and positive DIASs shrinks. In addition, the velocity of soliton decreases with increasing
for the coexistence of negative and positive DIASs shrinks. In addition, the velocity of soliton decreases with increasing 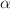 and electron concentration
and electron concentration 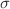 , regardless of soliton polarity. On the other hand, the width of positive DIASs decreases with the increase of
, regardless of soliton polarity. On the other hand, the width of positive DIASs decreases with the increase of  , whereas the one negative solitons take an opposite way. Moreover, the width of DIASs varies non-monotonous with respect to the cutoff parameter. Based on the parameters within Saturn’s magnetosphere, the strength of the electric field with DIAS can explain the observations made within Saturn’s magnetosphere. The present investigation may be useful in the understanding of the properties of localized nonlinear electrostatic structure in space dusty plasma with nonthermal electrons.
, whereas the one negative solitons take an opposite way. Moreover, the width of DIASs varies non-monotonous with respect to the cutoff parameter. Based on the parameters within Saturn’s magnetosphere, the strength of the electric field with DIAS can explain the observations made within Saturn’s magnetosphere. The present investigation may be useful in the understanding of the properties of localized nonlinear electrostatic structure in space dusty plasma with nonthermal electrons.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.