https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00947-y
Regular Article - Optical Phenomena and Photonics
Morphology-dependent resonances in three-layered spherical particle
1
Public Experiment Center, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 200093, Shanghai, China
2
College of Science, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, 200093, Shanghai, China
Received:
27
September
2024
Accepted:
11
December
2024
Published online:
12
July
2025
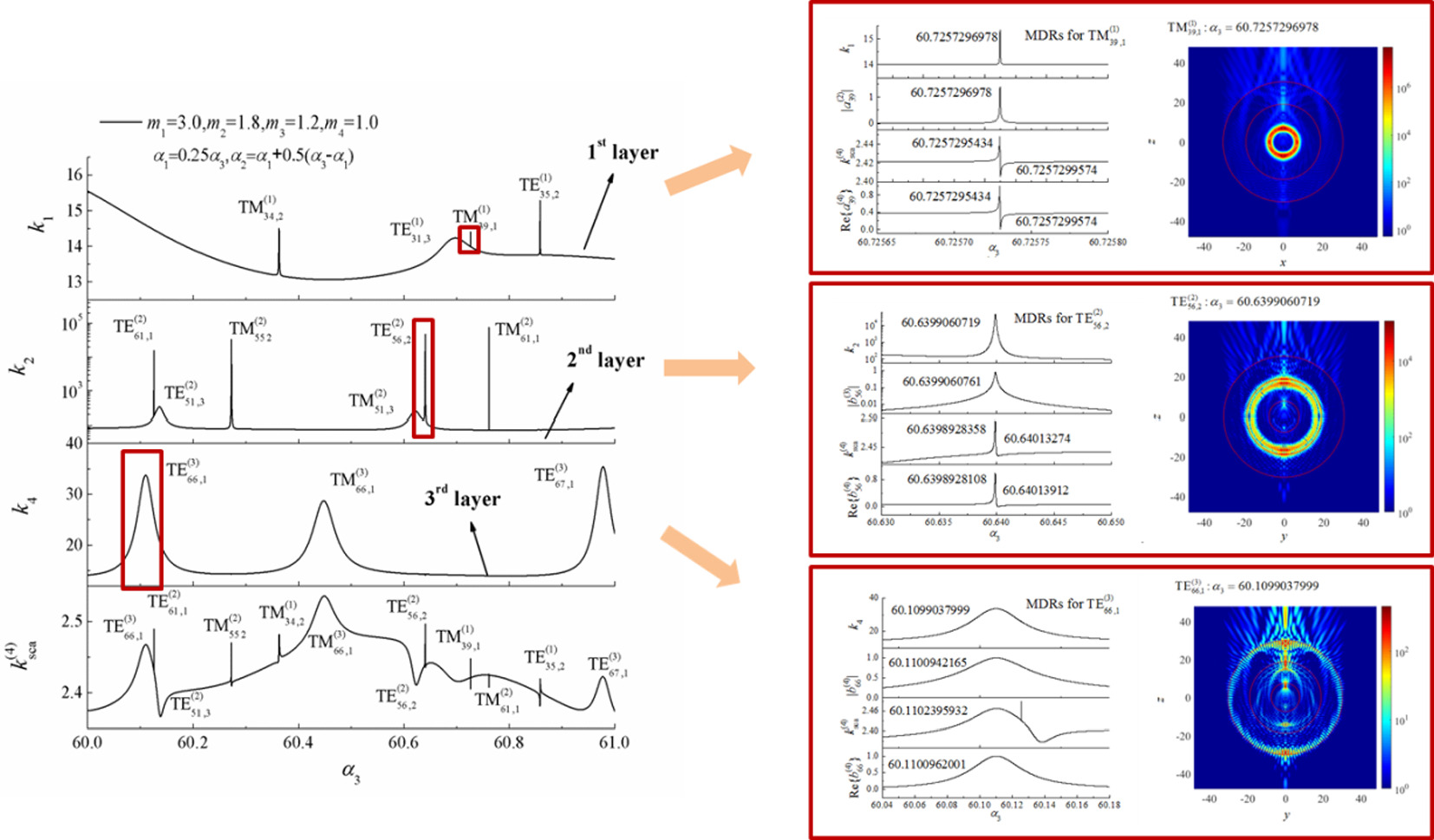
Multilayered spherical particles play a significant role in modern science and technology. Morphology-dependent resonances (MDRs) in these particles are critical due to their extensive applications across various fields. However, the complexity of MDRs in multilayered spherical particles surpasses that of homogeneous particles. As a result, existing models mainly focus on MDRs in homogeneous particles or MDRs at the outermost interior interface of coated or multilayered sphere particles. In this paper, MDRs in three-layered spherical particles are investigated by reformulating the internal scattering efficiency of each layer. This redefinition allows for an independent and straightforward analysis of resonances layer-by-layer, enabling researchers to examine the resonance characteristics of specific inner layers and accurately identify resonance locations. The study explores the relationships between MDRs in each layer, outermost scattering efficiency and partial wave to confirm the source of resonance. The findings of this study provide a theoretical foundation for studying MDRs of multilayered particles and their measurement.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.