https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-025-01007-9
Regular Article - Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Comprehensive study on the electron-impact ionization cross sections of neutral beryllium (Be) and its ions
1
Department of Physics, University College of Science, Mohanlal Sukhadia University, 313001, Udaipur, India
2
National Institute for Fusion Science, National Institutes of Natural Sciences, 322-6 Oroshi-Cho, 509-5292, Toki, Gifu, Japan
3
Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Engineering and Sciences, Kyushu University, 816-8580, Kasuga, Fukuoka, Japan
a ghanshyam.purohit@mlsu.ac.in, gvpurohit1974@gmail.com
Received:
25
January
2025
Accepted:
28
April
2025
Published online:
27
May
2025
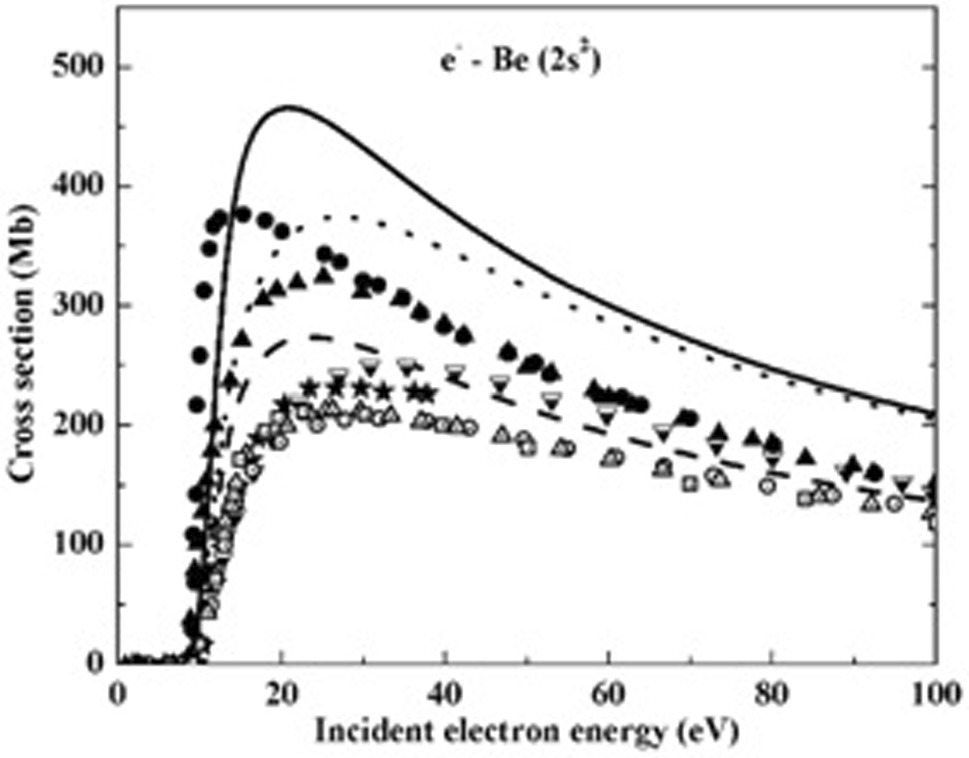
The electron-impact ionization cross sections are reported for neutral beryllium (Be) and its ions (Be⁺, Be2⁺, and Be3⁺) within the frameworks of the Binary Encounter Dipole (BED), Coulomb-Born Exchange (CBE), and Distorted Wave (DW) methods. The ionization cross sections have been calculated for energies ranging from the ionization threshold up to 100 eV, considering both the ground state and the first excited state of beryllium. The BED method exhibited excellent agreement with the experimental data for Be⁺ within the energy range of 52–116 eV. Furthermore, a detailed comparison has been performed between the calculated cross sections and existing theoretical and experimental data. We have additionally calculated the Maxwell rate coefficients for direct ionization in the ground state of neutral beryllium (Be) and its ions over an electron energy range extending up to 10 keV. These results provide valuable insights for plasma modeling by offering critical data for understanding the interaction dynamics of beryllium in plasma environments.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2025
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.