https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00914-7
Regular Article - Atomic Physics
Breit interaction in dielectronic recombination of hydrogenlike xenon ions: storage-ring experiment and theory
1
I. Physikalisches Institut, Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen, 35392, Giessen, Germany
2
Helmholtz Forschungsakademie Hessen für FAIR (HFHF), GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, Campus Gießen, 35392, Giessen, Germany
3
GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung, 64291, Darmstadt, Germany
4
Helmholtz-Institut Jena, 07743, Jena, Germany
5
Institut für Theoretische Physik, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, 07743, Jena, Germany
6
Institut für theoretische Physik, Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen, 35392, Giessen, Germany
7
Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, 69117, Heidelberg, Germany
Received:
24
July
2024
Accepted:
11
September
2024
Published online:
1
October
2024
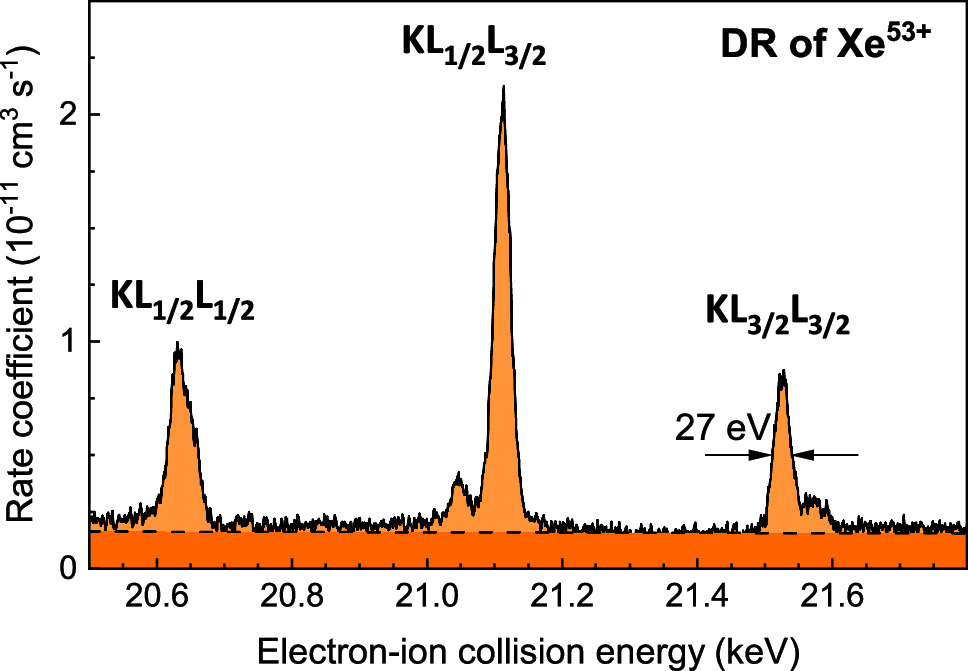
Electron-ion collision spectroscopy of the KLL dielectronic recombination (DR) resonances of hydrogenlike xenon ions was performed at a heavy-ion storage ring with a resolving power that is competitive with x-ray spectroscopy of inner-shell transitions in highly charged ions. The 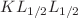 ,
, 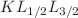 , and
, and  resonance groups and even parts of their fine structure are individually resolved. The resonance strengths were measured on an absolute scale and compared with results from multi-configuration Dirac–Fock (MCDF) calculations. These are in excellent agreement with the experimental findings when QED effects on the resonance energies and the Breit interaction are considered. As already found for DR of hydrogenlike uranium (Bernhardt et al. in Phys Rev A 83:020701(R), 2011), this interaction is particularly strong for the
resonance groups and even parts of their fine structure are individually resolved. The resonance strengths were measured on an absolute scale and compared with results from multi-configuration Dirac–Fock (MCDF) calculations. These are in excellent agreement with the experimental findings when QED effects on the resonance energies and the Breit interaction are considered. As already found for DR of hydrogenlike uranium (Bernhardt et al. in Phys Rev A 83:020701(R), 2011), this interaction is particularly strong for the 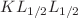 resonance group. For U
resonance group. For U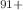 , it increases the
, it increases the 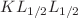 DR resonance strength by 40%. For Xe
DR resonance strength by 40%. For Xe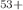 , the increase is found to amount to 25%, confirming the prediction that the influence of the Breit interaction grows with increasing nuclear charge. A comprehensive appendix treats the derivation of experimental and theoretical merged-beams recombination rate coefficients for interacting beams of relativistic electrons and ions.
, the increase is found to amount to 25%, confirming the prediction that the influence of the Breit interaction grows with increasing nuclear charge. A comprehensive appendix treats the derivation of experimental and theoretical merged-beams recombination rate coefficients for interacting beams of relativistic electrons and ions.
© The Author(s) 2024
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.