https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00903-w
Regular Article – Clusters and Nanostructures
Global lowest energy structures and electronic properties of InnM (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, n = 6–9) clusters
College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Northwest Normal University, 730070, Lanzhou, China
Received:
8
June
2024
Accepted:
8
August
2024
Published online:
16
September
2024
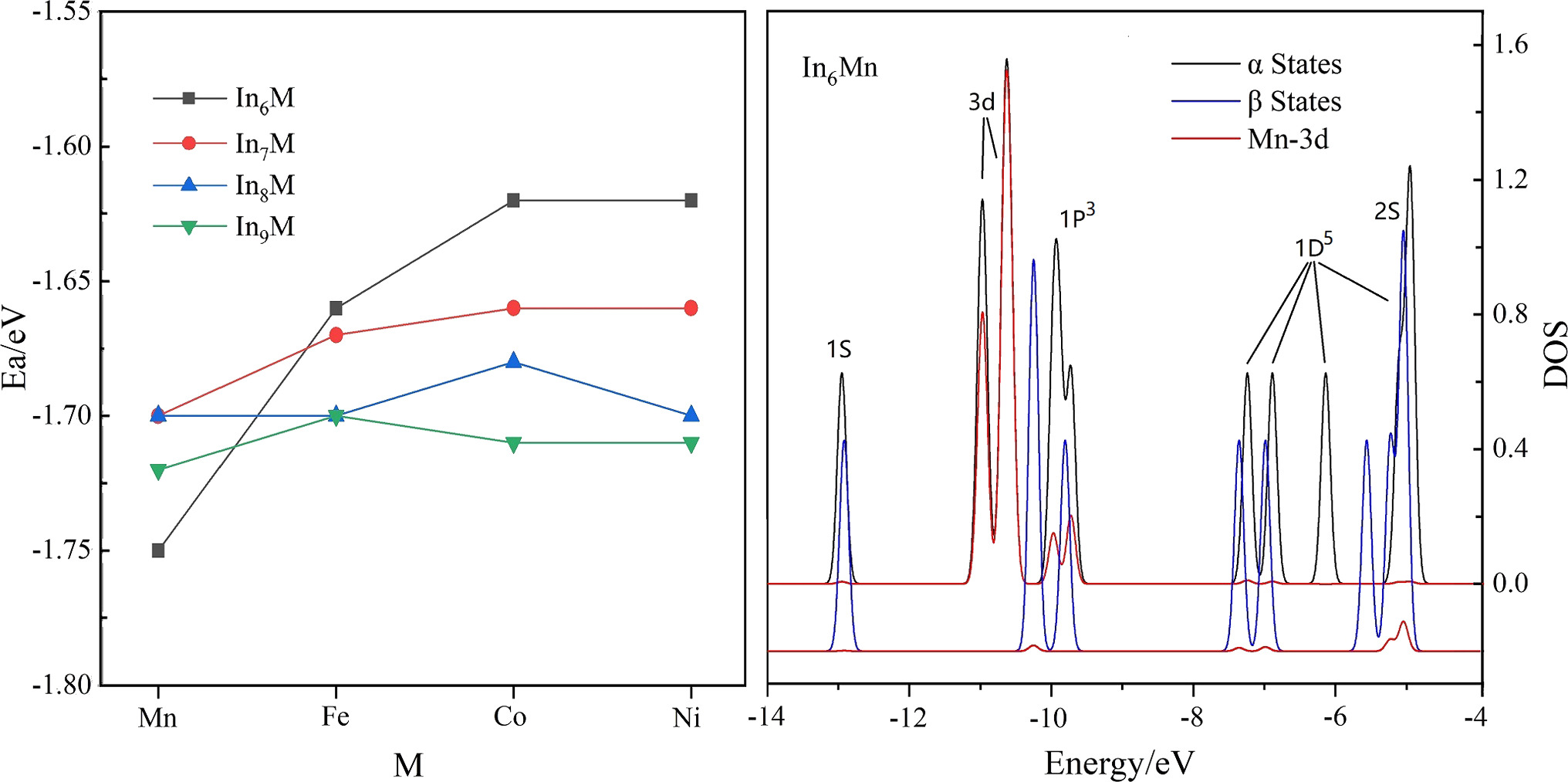
The global lowest-energy structures of the transition metal (TM) doped InnM (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, n = 6–9) clusters are studied by using genetic algorithm combined with spin-polarized density functional theories. The low energy structures suggest that the basic building units of InnM in this size range are TM doped triangular prism and octahedron. For the lowest energy isomers, the TM atoms are endohedrally doped in In8Co/Ni and In9Fe and exohedrally doped in other clusters. Charge density analysis shows that Mn atom offers electron to the Inn frames but Co and Ni accept electrons. The spin multiplicities of the lowest energy structures are the same with those of the TM atoms for the exohedrally doped InnM clusters for n = 6, 8, and the values are smaller by one for the endohedrally doped clusters. The molecular orbitals and density of states reveal that the 4s2 electrons of the TM atoms and the 5s25p valence electrons of the In atoms form superatomic orbitals consistent with the jellium model, but the 3d orbitals of the TM interact with the superatomic orbitals in different manners and are generally singly occupied.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00903-w.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.