https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00851-5
Regular Article - Atomic Physics
High repetition rate sub-ns electron pulses from pulsed-resonance Rydberg field-ionization (PRRFI)
1
Université Paris-Saclay, CNRS, Laboratoire Aimé Cotton, 91405, Orsay, France
2
Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences, ETH Zurich, CH-8093, Zurich, Switzerland
b
daniel.comparat@universite-paris-saclay.fr
Received:
21
March
2024
Accepted:
18
April
2024
Published online:
1
June
2024
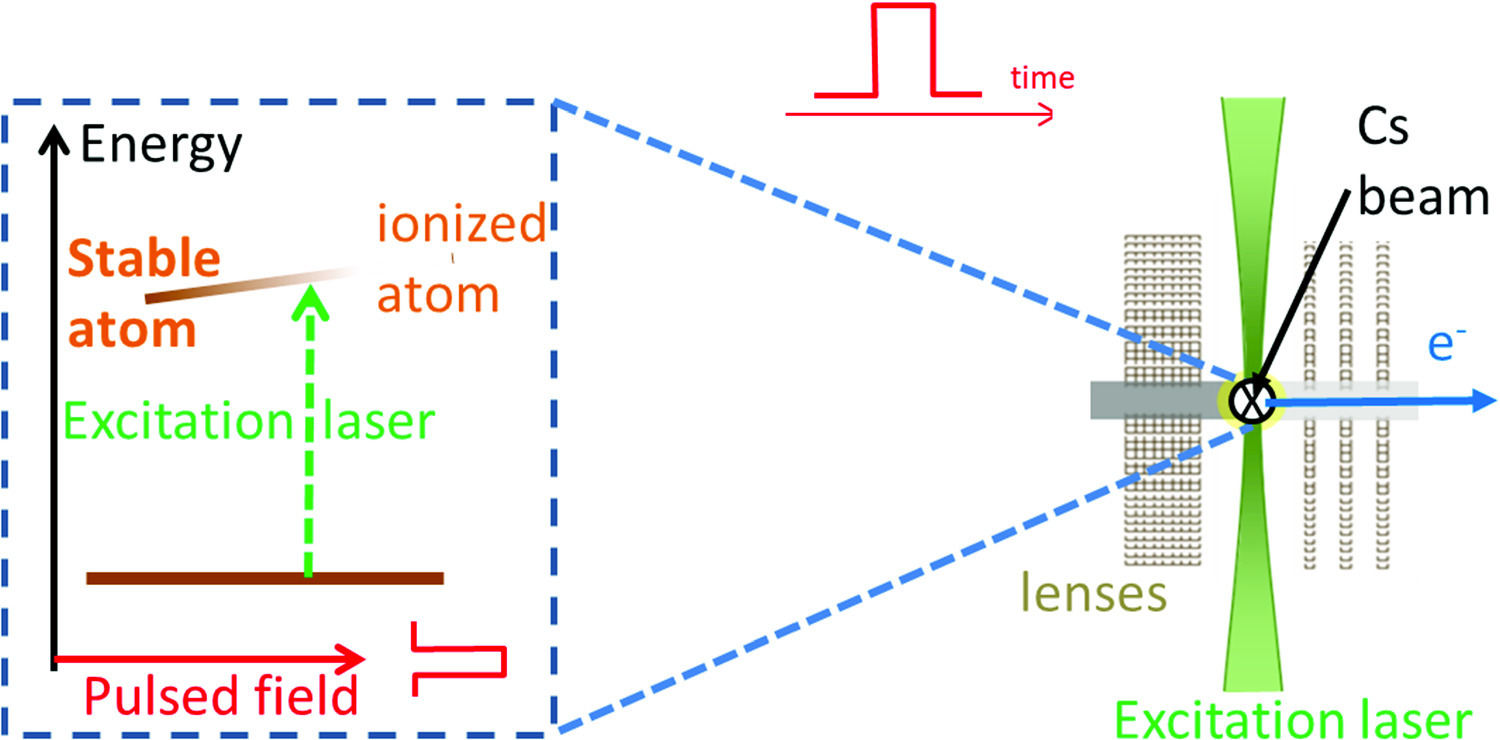
We demonstrate a novel technique, Pulsed-Resonance Rydberg Field-ionization (PRRFI), to generate low-energy electron bunches at high repetition rates. By combining continuous-wave laser excitation with a pulsed electric field, this method selectively ionizes Rydberg–Stark states in cesium atoms, producing sub-ns long electron bunches (down to 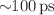 ) at a repetition rate of
) at a repetition rate of 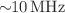 . The method is demonstrated to offer significant advantages in terms of flexibility in the ionization repetition rate and pulse delay adjustments. The PRRFI method holds promises for applications in high-resolution electron microscopy and spectroscopy, potentially for overcoming the limitations of traditional electron sources in terms of brightness and energy spread.
. The method is demonstrated to offer significant advantages in terms of flexibility in the ionization repetition rate and pulse delay adjustments. The PRRFI method holds promises for applications in high-resolution electron microscopy and spectroscopy, potentially for overcoming the limitations of traditional electron sources in terms of brightness and energy spread.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.