https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00815-9
Regular Article - Atomic Physics
Photoionization process of energy-dependent excited He atom trapped inside endofullerene molecules encased in a quantum plasma
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Sivas Cumhuriyet University, 58140, Sivas, Turkey
Received:
23
November
2023
Accepted:
5
February
2024
Published online:
21
February
2024
We consider the excited He atom 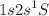 (He
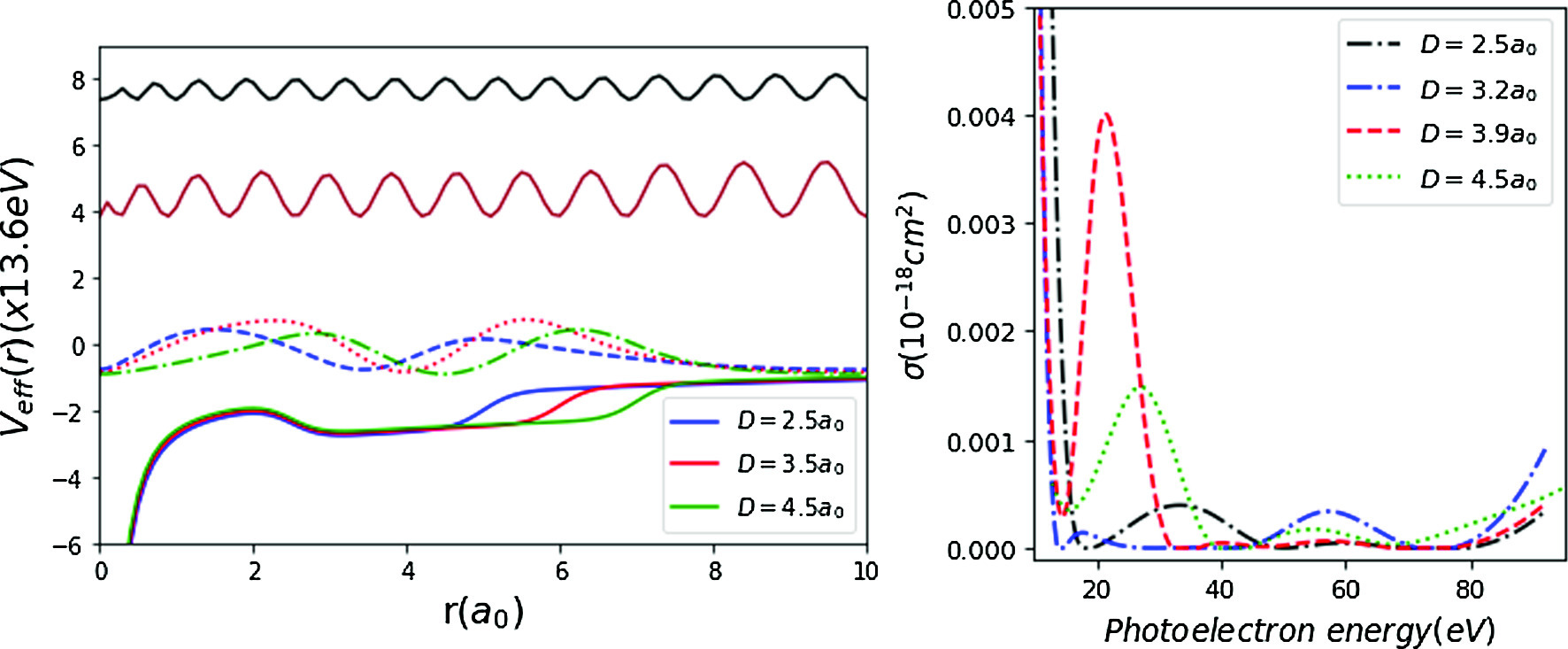
(He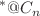 ) trapped within an energy-dependent endohedral fullerene, encased in a quantum plasma described by the more general exponential cosine screened Coulomb (MGECSC) potential, under a spherical confinement. The nonrelativistic wave equation is solved using the Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg (RKF) method, and discrete and continuum spectra along with the corresponding wave functions are obtained. The screening effect of the plasma medium, endohedral trapping, and the shifted effect due to energy-dependence modify the effective potential energy of the system, influencing the localization of discrete and continuum states and leading to various overlapping scenarios. The new localizations, various overlapping cases, and interference of outgoing and scattering photoelectron waves lead to explicit confinement resonances. Considering these resonances, peaks in the photoionization cross sections (PCSs) are analyzed. This analysis provides significant details for the photoionization dynamics of the artificial system He
) trapped within an energy-dependent endohedral fullerene, encased in a quantum plasma described by the more general exponential cosine screened Coulomb (MGECSC) potential, under a spherical confinement. The nonrelativistic wave equation is solved using the Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg (RKF) method, and discrete and continuum spectra along with the corresponding wave functions are obtained. The screening effect of the plasma medium, endohedral trapping, and the shifted effect due to energy-dependence modify the effective potential energy of the system, influencing the localization of discrete and continuum states and leading to various overlapping scenarios. The new localizations, various overlapping cases, and interference of outgoing and scattering photoelectron waves lead to explicit confinement resonances. Considering these resonances, peaks in the photoionization cross sections (PCSs) are analyzed. This analysis provides significant details for the photoionization dynamics of the artificial system He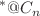 . The relevant ranges and critical values of plasma, endohedral encapsulation, and energy dependence parameters in the process of formation of these resonances and during PCS investigations are explained. Additionally, the cross section curves, resonance positions, effective photoelectron energy range, and overall PCS behaviors are described. This information can be important for potential experiments, in addition to other theoretical investigations. This information can be crucial not only for further theoretical investigations but also for potential experiments.
. The relevant ranges and critical values of plasma, endohedral encapsulation, and energy dependence parameters in the process of formation of these resonances and during PCS investigations are explained. Additionally, the cross section curves, resonance positions, effective photoelectron energy range, and overall PCS behaviors are described. This information can be important for potential experiments, in addition to other theoretical investigations. This information can be crucial not only for further theoretical investigations but also for potential experiments.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.