https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-024-00811-z
Regular Article - Quantum Optics
A design and comparative investigation of graded AlxGa1 − x N QB for W-Al0.58GaN/W-Al0.64–0.58 GaN DUV laser diode on AlN substrate
1
National Center for International Joint Research of Electronic Materials and Systems, International Joint-Laboratory of Electronic Materials and Systems of Henan Province, School of Electrical and Information Engineering, Zhengzhou University, 450001, Zhengzhou, Henan, People’s Republic of China
2
Department of Physics, Bacha Khan University, 24420, Charsadda, KPK, Pakistan
3
Institute of Intelligence Sensing, Zhengzhou University, 450001, Zhengzhou, Henan, People’s Republic of China
4
Research Institute of Industrial Technology Co. Ltd., Zhengzhou University, 450001, Zhengzhou, Henan, People’s Republic of China
5
Zhengzhou Way Do Electronics Co. Ltd., 450001, Zhengzhou, Henan, People’s Republic of China
Received:
20
October
2023
Accepted:
29
January
2024
Published online:
12
February
2024
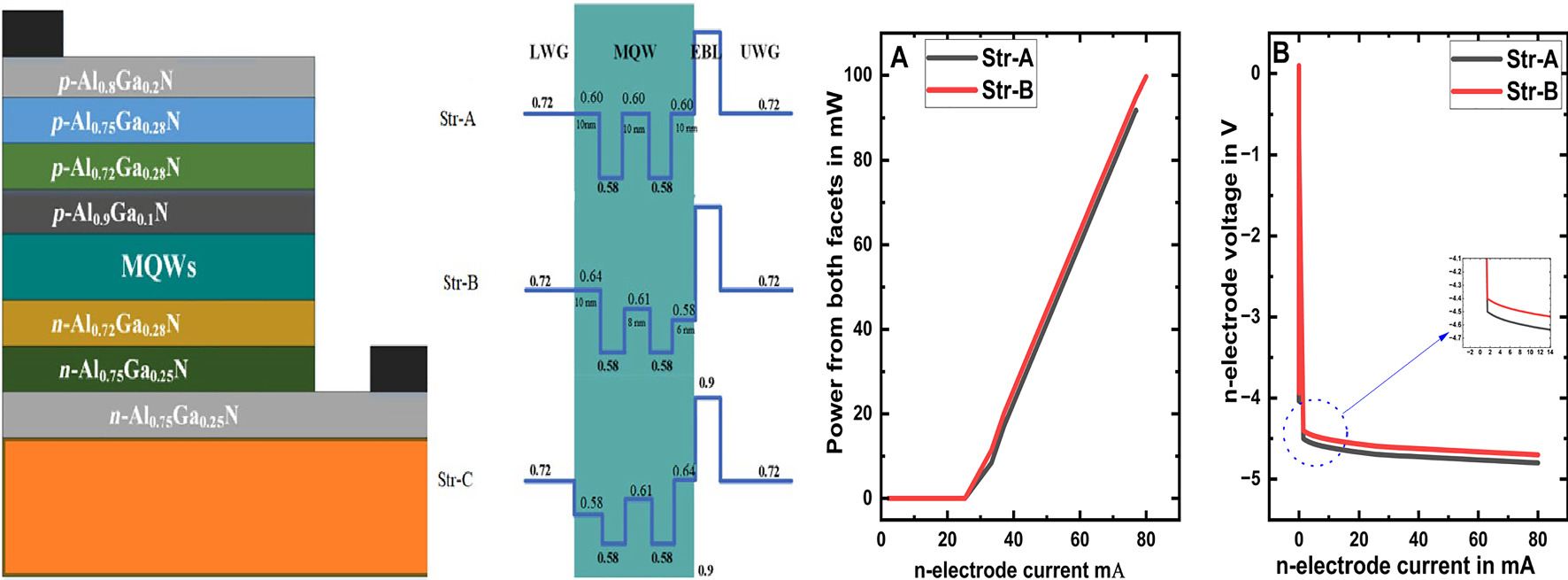
In this study, we aim to improve the efficiency of AlGaN-based deep-UV-LD by thickness grading and composition grading of the quantum barrier. We proposed the structure of DUV-LD, and then we conducted the simulation via LASTIP software to check the opto-electronics properties of the proposed structure. In the results, we observed that by decreasing the thickness grading and composition grading of the AlGaN-based deep-UV laser, the output power increased to 98 mW, the conduction band barrier height increased to 570 meV, the intensity of device, hole-current density, and the stimulated recombination rate also increased. However, by decreasing the thickness and composition grading of the AlGaN-semiconductor-based deep-UV-LD, valence band barrier height 132 meV, threshold voltage 4.43 V, threshold current 25.27 mA, and electron current density also decreased. It shows that if the composition grading of AlGaN-based DUV-LD decreases, then the performance of the device increases.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.