https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00796-1
Regular Article - Quantum Optics
Measurement-assisted non-Gaussian gate for Schrödinger cat states preparation: Fock resource state versus cubic phase state
1
Saint Petersburg State University, Universitetskaya nab. 7/9, 199034, Saint Petersburg, Russia
2
Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU), Polytechnicheskaya 29, 195251, Saint Petersburg, Russia
3
Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Innsbruck, Technikerstraße 21a, 6020, Innsbruck, Austria
c
natalia.masalaeva@uibk.ac.at
Received:
16
October
2023
Accepted:
24
December
2023
Published online:
27
January
2024
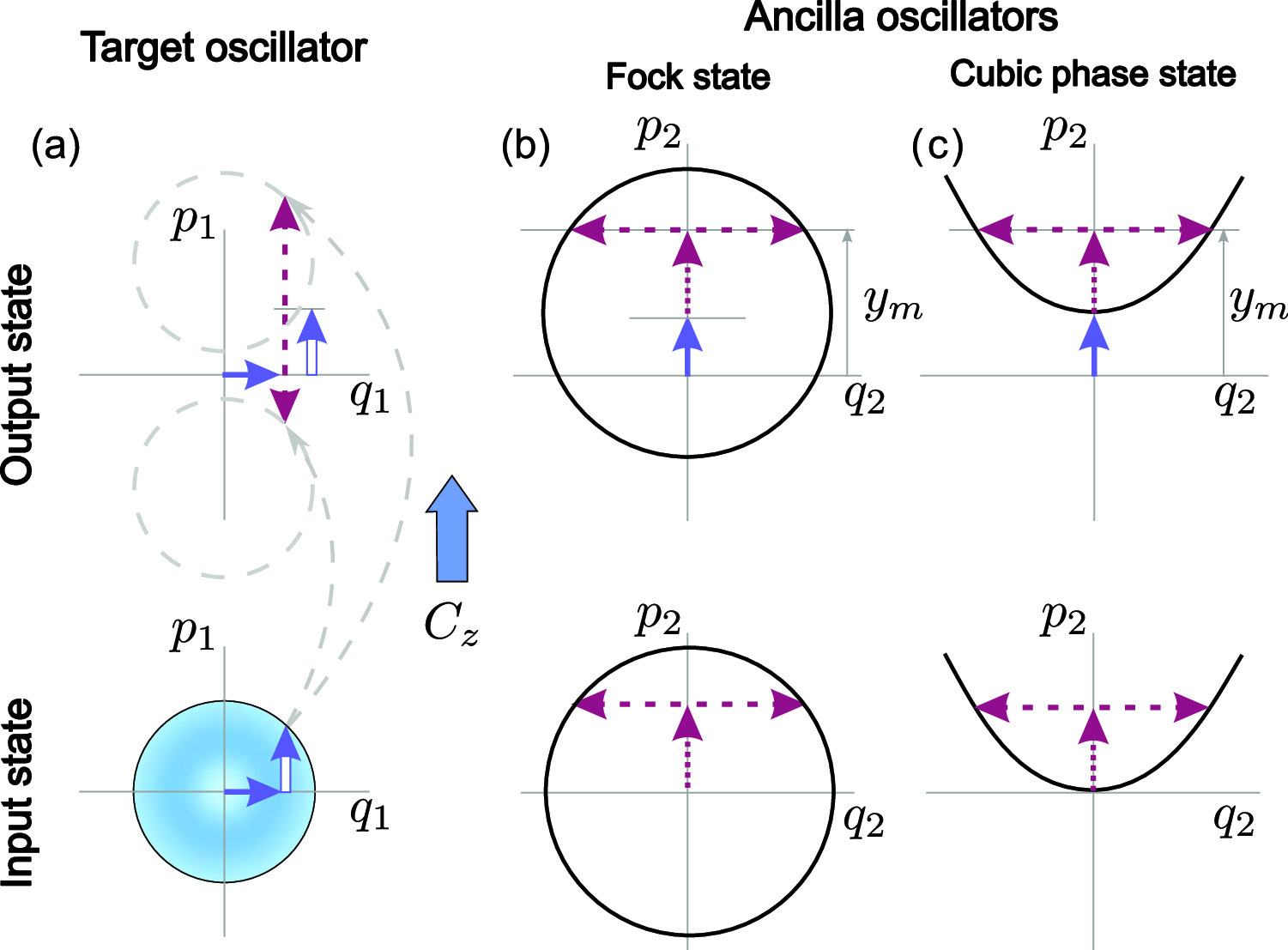
In this paper, we consider the preparation of Schrödinger cat states using a measurement-assisted gate based on the Fock resource state, the quantum non-demolition entangling operation, and the homodyne measurement. Previously, we have investigated the gate, which for the same goal uses the ancillary non-Gaussian cubic phase state generated from quadrature squeezed states at realistic (finite) squeezing. It is of evident interest to compare the efficiency of both schemes, that is, their ability to produce cat-like superpositions with high fidelity and probability of success. We introduce, in parallel with the exact theoretical description of the gate operation, a clear visual interpretation of the output state based on the semiclassical mapping of the input field variables. The emergence of the superpositions of “copies” of the input state in both schemes is due to the fact that such mapping is compatible with two (or, in general, more) sets of values of the output field observables. We demonstrate that even fine details of the output of both gates are effectively predicted and interpreted in our approach. We examine the fidelity and success probability and reveal the ranges of physical parameters where the Fock state-based and the cubic phase state-based gates demonstrate comparable fidelity and (or) probability of success.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.