https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00783-6
Regular Article – Ultraintense and Ultrashort Laser Fields
Energetic neutral particle generation by laser using gold nanorod embedded CH foil
Department of Physics, Amity Institute of Applied Sciences, Amity University, 201303, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India
Received:
7
July
2023
Accepted:
10
November
2023
Published online:
4
December
2023
We propose a new scheme of a few MeV range uni-directional neutral particle generation via charge exchange mechanism (Rajeev et al. in Nat Phys 9:185, 2013) of energetic ions driven by intense laser. A two-dimensional stack of gold nanorods, embedded inside a hydrocarbon foil (CH), are ionized by the action of pulse of intensities more than 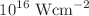 . The pre-pulse is diverted toward a gaseous/clustered environment and excites atoms/clusters to Rydberg states, while the main part of the pulse exerts a transverse ponderomotive force on electrons causing its immediate expulsion. Under Coulomb explosion, carbon ions and protons exit quickly, while the gold ions remain practically immobile due to inertia. The potential structure created by the positively charged nano-rod assembly has complete transverse confinement and axial acceleration. Carbon ions and protons are axially accelerated and undergo collision with Rydberg state atoms/cluster causing charge exchange. This scheme addresses the issues of complete transverse confinement, directionality, and in-situ charge exchange environment. Typical 40 femtosecond pulses with normalized amplitude (
. The pre-pulse is diverted toward a gaseous/clustered environment and excites atoms/clusters to Rydberg states, while the main part of the pulse exerts a transverse ponderomotive force on electrons causing its immediate expulsion. Under Coulomb explosion, carbon ions and protons exit quickly, while the gold ions remain practically immobile due to inertia. The potential structure created by the positively charged nano-rod assembly has complete transverse confinement and axial acceleration. Carbon ions and protons are axially accelerated and undergo collision with Rydberg state atoms/cluster causing charge exchange. This scheme addresses the issues of complete transverse confinement, directionality, and in-situ charge exchange environment. Typical 40 femtosecond pulses with normalized amplitude ( ) can generate energetic neutrals of
) can generate energetic neutrals of  range. In the present scheme, one also gets the flexibility of using the changed nanorod geometry or alignment or using external magnetic field to control the beam direction prior to charge exchange stage.
range. In the present scheme, one also gets the flexibility of using the changed nanorod geometry or alignment or using external magnetic field to control the beam direction prior to charge exchange stage.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





