https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00767-6
Regular Article – Clusters and Nanostructures
Stability and electronic structure of the magnetic hyperhalogen Fe(BF4)4
College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Northwest Normal University, 730070, Lanzhou, China
Received:
1
August
2023
Accepted:
8
October
2023
Published online:
25
October
2023
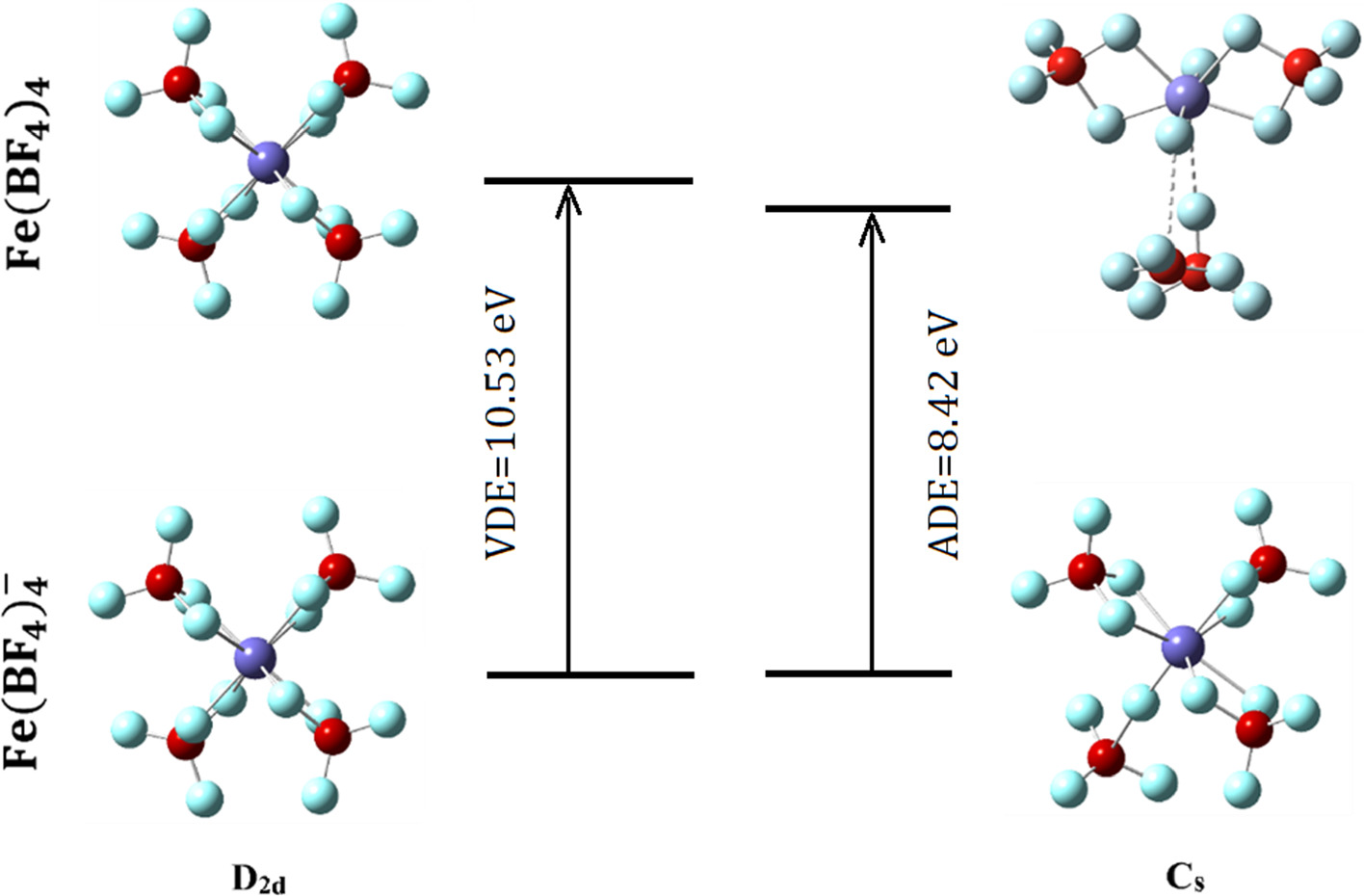
FeCl4− and BF4− are very stable superhalogen anions, and FeCl4− possesses a magnetic moment of 5 μB due to the singly occupied 3d5 orbitals of the Fe3+. This letter determines the lowest energy structures and stabilities of anionic and neutral Fe(BF4)4−/0 and investigates the magnetic hyperhalogen property by using density function theories and configuration interaction method. The binding and dissociation energies indicate that both the anionic and neutral species are stable. The most stable structure of the anion has D2d symmetry in which the four BF4 units are coordinated to the central Fe atom in bidentate manner. The vertical and adiabatic detachment energies of Fe(BF4)4− reach 10.53 and 9.76 eV, respectively. The 3d orbitals of the central Fe atom form strong covalent bonds with the BF4 units, and the magnetic moments (5 μB) are formed by delocalized spin orbitals.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.