https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00707-4
Regular Article – Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Low to high energy electron interactions with AlCl
1
Department of Physics, SGTB Khalsa College, University of Delhi, 110007, Delhi, India
2
Department of Physics, Bhaskaracharya College of Applied Sciences, University of Delhi, 110075, New Delhi, India
3
Department of Physics and Astrophysics, University of Delhi, 110007, Delhi, India
Received:
6
March
2023
Accepted:
16
June
2023
Published online:
21
July
2023
Various cross sections due to electron-impact are reported for aluminum monochloride (Al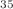 Cl) from low to high energy range. The scattering calculations in the low energy range (less than ionization) are accomplished using the well-known R-matrix method. Different scattering models are used to assess the convergence of results and to analyse the formation of resonances. All models converge around 4 eV, showing that the impact of correlation-polarization ceases on scattering. The shape resonance is observed in static-exchange model in the
Cl) from low to high energy range. The scattering calculations in the low energy range (less than ionization) are accomplished using the well-known R-matrix method. Different scattering models are used to assess the convergence of results and to analyse the formation of resonances. All models converge around 4 eV, showing that the impact of correlation-polarization ceases on scattering. The shape resonance is observed in static-exchange model in the 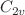 point group corresponding to
point group corresponding to 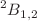 scattering symmetry. It becomes a bound state in static-exchange-polarization model. In 18-states close-coupling model, this resonance state is almost bound. The elastic differential, integral and momentum transfer cross sections beyond ionization threshold are reported by using local potential-based single-center-expansion approach. A near overlapping nature of elastic cross sections is noticed from two different theories at the ionization threshold. This helps to predict the estimates of elastic cross sections over a broad energy range. The ionization cross sections are computed adopting the semi-empirical binary-encounter-Bethe model for electrons. The dissociative electron attachment process is also discussed.
scattering symmetry. It becomes a bound state in static-exchange-polarization model. In 18-states close-coupling model, this resonance state is almost bound. The elastic differential, integral and momentum transfer cross sections beyond ionization threshold are reported by using local potential-based single-center-expansion approach. A near overlapping nature of elastic cross sections is noticed from two different theories at the ionization threshold. This helps to predict the estimates of elastic cross sections over a broad energy range. The ionization cross sections are computed adopting the semi-empirical binary-encounter-Bethe model for electrons. The dissociative electron attachment process is also discussed.
K. L. Baluja: Retired Professor.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.




