https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00697-3
Regular Article - Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Methylation and isomerization effects on the elastic electron scattering cross sections by H O
O and C
and C H
H O
O
1
Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Caixa Postal 19044, 81531-980, Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil
2
Centro de Ciências Naturais e Humanas, Universidade Federal do ABC, Santo André, Brazil
d
romarly.costa@ufabc.edu.br
e
bettega@fisica.ufpr.br
Received:
17
April
2023
Accepted:
2
June
2023
Published online:
26
June
2023
Integral, differential and momentum-transfer elastic cross sections for the scattering of low-energy electrons by hydrogen peroxide (HP), dimethyl peroxide (DMP) and ethylene glycol (ETG) are reported. These cross sections were calculated in the static-exchange and static-exchange plus polarization approximations for energies up to 30 eV by using the Schwinger multichannel method implemented with norm-conserving pseudopotentials. Through the symmetry decomposition of the integral cross section according to the C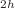 point group and the diagonalization of the scattering Hamiltonian, shape resonances were assigned to all three molecules. One shape resonance, namely
point group and the diagonalization of the scattering Hamiltonian, shape resonances were assigned to all three molecules. One shape resonance, namely 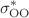 of
of 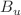 symmetry, was observed for HP around 2.5 eV. Due to the elongation of the O–O bond, when methyl groups are added to HP to form DMP, this resonance is shifted toward 2.1 eV in the DMP integral cross section. For DMP and ETG, a second peak, a broad structure that originates from the superposition of shape resonances of
symmetry, was observed for HP around 2.5 eV. Due to the elongation of the O–O bond, when methyl groups are added to HP to form DMP, this resonance is shifted toward 2.1 eV in the DMP integral cross section. For DMP and ETG, a second peak, a broad structure that originates from the superposition of shape resonances of 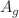 ,
, 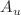 and
and 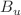 symmetries, was observed for higher impact energies. By comparing the cross sections of DMP and ETG, we found that the most striking differences appear in the low-energy regime, while for higher impact energies the cross sections are very similar, as expected for isomers.
symmetries, was observed for higher impact energies. By comparing the cross sections of DMP and ETG, we found that the most striking differences appear in the low-energy regime, while for higher impact energies the cross sections are very similar, as expected for isomers.
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.





