https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00344-3
Regular Article – Optical Phenomena and Photonics
Optimization of porous silicon structure as antireflective material
1
Institute of Intelligent Flexible Mechatronics, Jiangsu University, 212013, Zhenjiang, People’s Republic of China
2
National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, 210093, Nanjing, People’s Republic of China
a
gedaohan@mail.ujs.edu.cn
e
zhanglq4158@ujs.edu.cn
Received:
14
November
2021
Accepted:
11
January
2022
Published online:
11
February
2022
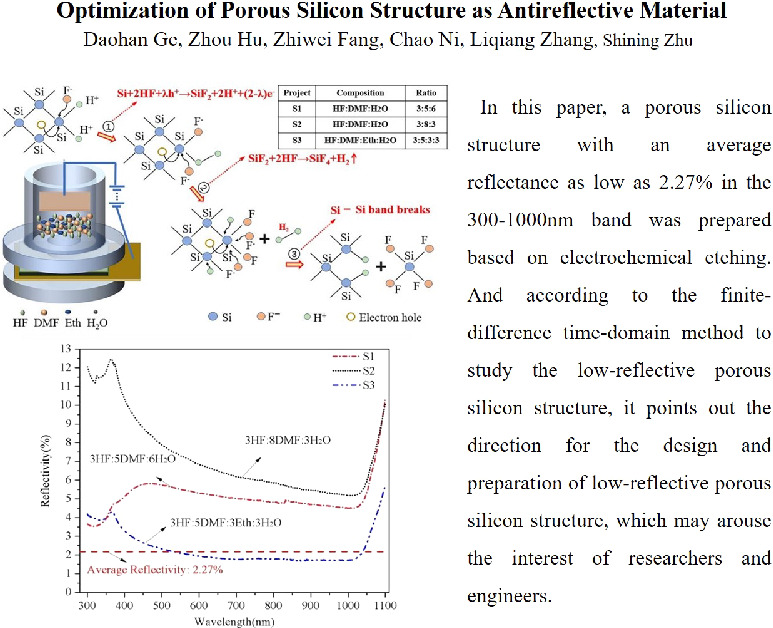
The porous silicon structures can effectively trap light by virtue of the large number of pore on its surface. Therefore, it is widely used in the fields of optical applications such as photoelectric conversion, photon collection and detection. A microporous silicon with an ultra-high antireflection performance was fabricated by using electrochemical etching based on the inrush current model. The results show that the porous silicon structure had a smaller pore size range, and the reflectivity of the porous silicon was reduced to 2.27% under light radiation with a wave length of 300–1000 nm. The surface reflectivity of porous silicon structure with different pore diameters and different aspect ratios was investigated by using the finite-difference time-domain method to reveal the antireflective mechanism. The porous silicon structure with high surface quality, high pore integrity, pore diameter distribution of 300–700 nm and the aspect ratio of the pore exceeds 4 was found to be beneficial in achieving lower reflectivity in the range of incident light wavelength from 300 to 1000 nm, which is useful for designing porous silicon antireflective material.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022