https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00341-6
Regular Article – Optical Phenomena and Photonics
Enhancing the optical absorption of Ga2SeTe Janus monolayer by adsorption of transition metals
National Institute of Technology, 136119, Kurukshetra, India
Received:
15
September
2021
Accepted:
6
January
2022
Published online:
1
February
2022
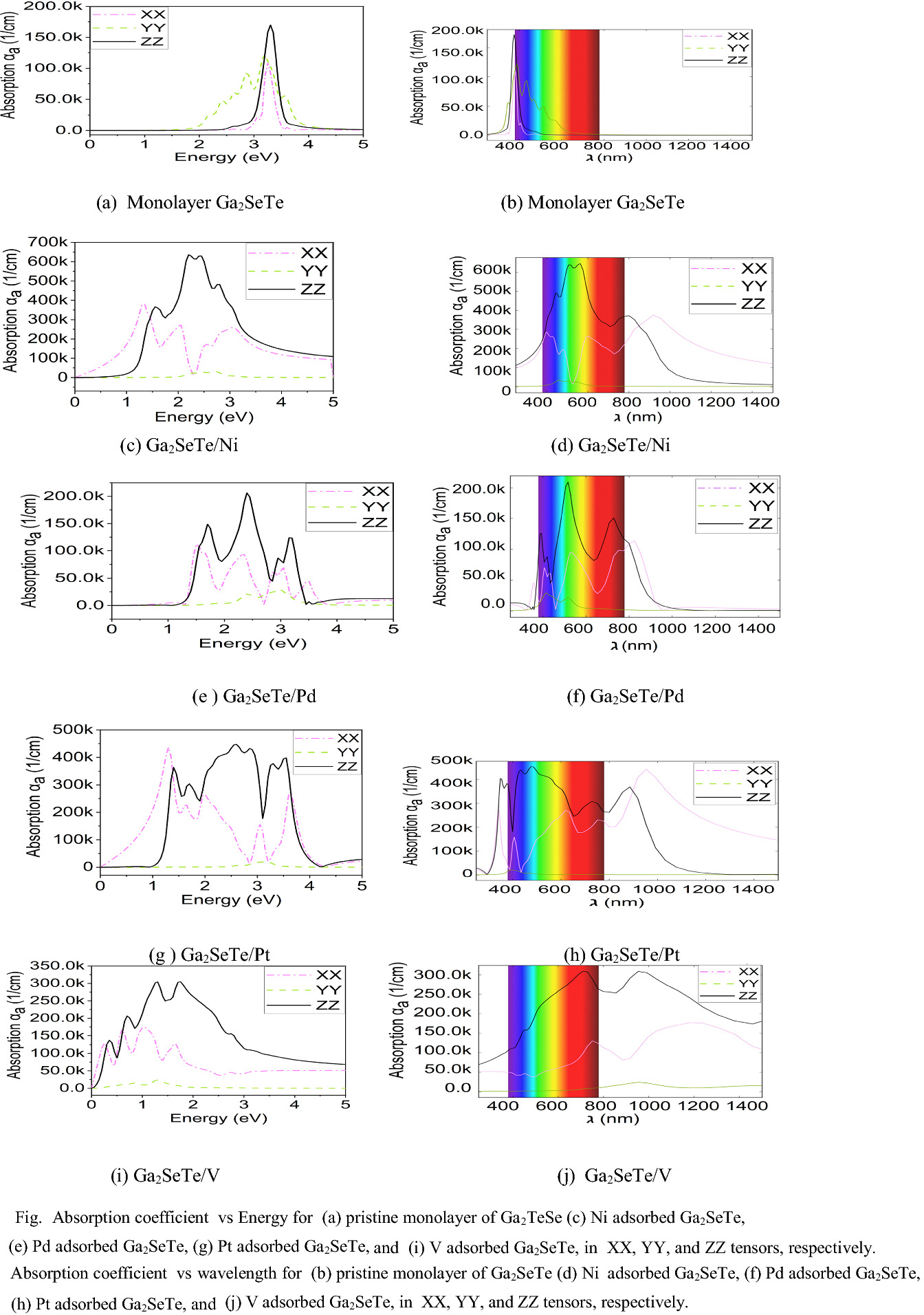
Optical and electronic properties of transition metal adsorbed Ga2SeTe Janus monolayer have been investigated in detail using DFT simulations. Results suggests that the pristine Janus monolayer of Ga2SeTe shows high absorption (− 15 × 104 1/cm) in few portions of the spectrum (− 380–430 nm). Metal adsorbed structures Ga2SeTe/Ni, Ga2SeTe/Pd, Ga2SeTe/Pt and Ga2SeTe/V results into redshift phenomena, which means that the absorption increases with the wavelength, or we can say that the absorption coefficient moved toward the red range of the spectrum. Absorption coefficient of Ni adsorbed structure is four times higher (− 60 × 104 1/cm) than the pristine Janus monolayer of Ga2SeTe. Considerably, higher absorption is also seen in other structures in the entire visible range (− 380–790 nm) of the spectrum. Dielectric function and refractive index of all metal adsorbed structures also calculated, and it is found that the absorption coefficient is in line with the dielectric constant. Due to its higher absorption peaks in the whole visible region, it is a potential candidate for optoelectronic applications and photovoltaic absorbers.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022