https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00242-0
Regular Article – Optical Phenomena and Photonics
Third-order optical nonlinearity in molybdenum trioxide ( )-doped vanadium pentaoxide (
)-doped vanadium pentaoxide ( ) thin films
) thin films
1
Laser Laboratory, Department of Physics, Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, 125001, Hisar, Haryana, India
2
Department of School Education, Hisar, Haryana, India
3
Instruments Research and Development Establishment (IRDE), Dehradun, Uttrakhand, India
Received:
21
May
2021
Accepted:
9
August
2021
Published online:
14
September
2021
The present work focuses on investigation of laser-induced third-order optical nonlinearity in molybdenum trioxide (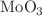 )-doped vanadium pentaoxide (
)-doped vanadium pentaoxide (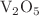 ) thin films.
) thin films. 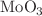 has been doped in
has been doped in 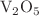 at different concentrations and thin films (
at different concentrations and thin films (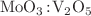 ) with varying thickness have been deposited on glass substrate by standard thermal evaporation method. X-ray diffraction studies show that deposited films have orthorhombic structure and the lattice parameters change with amount of doping as well as with the thickness of the film. A Nd:YAG-pulsed laser beam having wavelength
) with varying thickness have been deposited on glass substrate by standard thermal evaporation method. X-ray diffraction studies show that deposited films have orthorhombic structure and the lattice parameters change with amount of doping as well as with the thickness of the film. A Nd:YAG-pulsed laser beam having wavelength 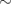 532nm has been used as excitation source. Intensity-dependent absorption coefficient (
532nm has been used as excitation source. Intensity-dependent absorption coefficient (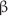 ), nonlinear refractive index (
), nonlinear refractive index (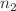 ) and cubic nonlinear susceptibility (
) and cubic nonlinear susceptibility (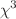 ) have been estimated using single-beam Z-scan technique. A concentration-dependent switching of optical nonlinearity has been observed occurring due to internal self-action effects. Optical limiting behavior has also been reported with limiting threshold (
) have been estimated using single-beam Z-scan technique. A concentration-dependent switching of optical nonlinearity has been observed occurring due to internal self-action effects. Optical limiting behavior has also been reported with limiting threshold ( ). Existence of strong third-order optical nonlinear susceptibility
). Existence of strong third-order optical nonlinear susceptibility 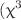 ) with quite low limiting threshold (
) with quite low limiting threshold ( ) for visible laser beam confirms that
) for visible laser beam confirms that 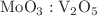 thin films have a great potential for the applications in photonic devices.
thin films have a great potential for the applications in photonic devices.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




