https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00133-4
Regular Article - Ultraintense and Ultrashort Laser Fields
High-order harmonic generation by aligned heteronuclear diatomic molecules in an orthogonally polarized two-color laser field
1
Faculty of Science, University of Sarajevo, Zmaja od Bosne 35, 71000, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
2
Max-Born-Institut for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy, Max-Born-Strasse 2a, 12489, Berlin, Germany
3
National Research Nuclear University MEPhI, Kashirskoe Shosse 31, 115409, Moscow, Russia
4
Academy of Sciences and Arts of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bistrik 7, 71000, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Received:
7
January
2021
Accepted:
24
March
2021
Published online:
9
April
2021
Using the molecular strong-field approximation, we investigate high-order harmonic generation by heteronuclear diatomic molecules exposed to an orthogonally polarized two-color laser field, which consists of two mutually orthogonal linearly polarized fields with frequencies 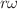 and
and  . Here, r and s are integers and
. Here, r and s are integers and 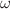 is the fundamental frequency. The harmonic emission rate and the harmonic ellipticity can be controlled using the laser-field parameters, in particular the relative phase and the intensity ratio of the laser-field components. The value of the relative phase, for which the emission rate is optimal, and the position of the cutoff can be estimated using a classical model. Also, we analyze the harmonic emission rate and the harmonic ellipticity as functions of the molecular orientation, which can also be used as a control parameter. Two types of minima are present in the spectra, depending on r and s. For
is the fundamental frequency. The harmonic emission rate and the harmonic ellipticity can be controlled using the laser-field parameters, in particular the relative phase and the intensity ratio of the laser-field components. The value of the relative phase, for which the emission rate is optimal, and the position of the cutoff can be estimated using a classical model. Also, we analyze the harmonic emission rate and the harmonic ellipticity as functions of the molecular orientation, which can also be used as a control parameter. Two types of minima are present in the spectra, depending on r and s. For  even, interference minima are present in the spectra of the T-matrix component either parallel or perpendicular to the internuclear axis. Using quantum-orbit theory and the saddle-point method, we derive a condition for the interference minima, which relates the molecular orientation angle
even, interference minima are present in the spectra of the T-matrix component either parallel or perpendicular to the internuclear axis. Using quantum-orbit theory and the saddle-point method, we derive a condition for the interference minima, which relates the molecular orientation angle  and the harmonic order n. The corresponding curves in the (
and the harmonic order n. The corresponding curves in the ( , n) plane well reproduce the minima of the numerically calculated spectra. For
, n) plane well reproduce the minima of the numerically calculated spectra. For  odd, minima are present in the spectra for a particular molecular orientation angle. These minima are explained using the explicit form of the T-matrix element. A heteronuclear as opposed to a homonuclear molecule affords a larger region in the parameter space where both the harmonic ellipticity and the harmonic intensity vary smoothly and both are large.
odd, minima are present in the spectra for a particular molecular orientation angle. These minima are explained using the explicit form of the T-matrix element. A heteronuclear as opposed to a homonuclear molecule affords a larger region in the parameter space where both the harmonic ellipticity and the harmonic intensity vary smoothly and both are large.
Quantum Aspects of Attoscience - edited by Carla Figueira de Morisson Faria, Andrew Brown, David B. Cassidy.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021




