https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2011-10601-y
Regular Article
Influence of dephasing on the entanglement teleportation via a two-qubit Heisenberg XYZ system
Quantum Optics Group, Department of Physics, University of
Isfahan, Hezar Jarib
Ave., Isfahan,
Iran
a
e-mail: h.r.mhmdi@gmail.com
Received:
20
October
2010
Received in final form:
16
January
2011
Published online:
25
March
2011
We study the entanglement dynamics of an anisotropic two-qubit Heisenberg XYZ system in
the presence of intrinsic decoherence. The usefulness of such a system for performance of
the quantum teleportation protocol 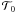 and entanglement teleportation protocol
and entanglement teleportation protocol 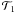 is also investigated. The results depend on the initial conditions and the parameters of
the system. The roles of system parameters such as the inhomogeneity of the magnetic field
b and the spin-orbit interaction parameter D, in
entanglement dynamics and fidelity of teleportation, are studied for both product and
maximally entangled initial states of the resource. We show that for the product and
maximally entangled initial states, increasing D amplifies the effects of
dephasing and hence decreases the asymptotic entanglement and fidelity of the
teleportation. For a product initial state and specific interval of the magnetic field
B, the asymptotic entanglement and hence the fidelity of teleportation
can be improved by increasing B. The XY and XYZ Heisenberg systems
provide a minimal resource entanglement, required for realizing efficient teleportation.
Also, in the absence of the magnetic field, the degree of entanglement is preserved for
the maximally entangled initial states
is also investigated. The results depend on the initial conditions and the parameters of
the system. The roles of system parameters such as the inhomogeneity of the magnetic field
b and the spin-orbit interaction parameter D, in
entanglement dynamics and fidelity of teleportation, are studied for both product and
maximally entangled initial states of the resource. We show that for the product and
maximally entangled initial states, increasing D amplifies the effects of
dephasing and hence decreases the asymptotic entanglement and fidelity of the
teleportation. For a product initial state and specific interval of the magnetic field
B, the asymptotic entanglement and hence the fidelity of teleportation
can be improved by increasing B. The XY and XYZ Heisenberg systems
provide a minimal resource entanglement, required for realizing efficient teleportation.
Also, in the absence of the magnetic field, the degree of entanglement is preserved for
the maximally entangled initial states 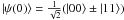 . The
same is true for the maximally entangled initial states
. The
same is true for the maximally entangled initial states
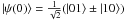 , in the
absence of spin-orbit interaction D and the inhomogeneity parameter
b. Therefore, it is possible to perform quantum teleportation protocol
, in the
absence of spin-orbit interaction D and the inhomogeneity parameter
b. Therefore, it is possible to perform quantum teleportation protocol
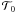 and entanglement teleportation
and entanglement teleportation 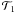 ,
with perfect quality, by choosing a proper set of parameters and employing one of these
maximally entangled robust states as the initial state of the resource.
,
with perfect quality, by choosing a proper set of parameters and employing one of these
maximally entangled robust states as the initial state of the resource.
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag 2011




