https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2010-10495-1
Plasma with two-negative ions and immobile dust particles: planar and non-planar ion-acoustic wave propagation
1
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science-Damietta, Mansoura University, New Damietta, 34517 Mansoura, Egypt
2
Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Port Said University, Port, Said, Egypt
Corresponding authors: a wmmoslem@hotmail.com wmm@tp4.rub.de
Received:
8
September
2010
Revised:
22
October
2010
Published online:
14
January
2011
By using the hydrodynamic equations of positive and two negative ions,
Boltzmann electron density distribution, and Poisson equation with immobile
positive/negative dust particles, a cylindrical Korteweg-de Vries (CKdV)
equation is derived for small but finite amplitude ion-acoustic waves. At the
critical total negative ion concentration and/or the critical density rate of
the second-negative ions, the pulses collapse at this limit as nonlinearity
fails to balance dispersion. Then the CKdV equation is not appropriate to
describe the system. Therefore, the modified CKdV (MCKdV) and extended CKdV
(ECKdV) equations are derived at the critical plasma compositions and in the
vicinity of the critical plasma compositions, respectively. The physical
parameters of two plasma environments (e.g., Xe+–F-–SF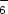 and
Ar+–F-–SF
and
Ar+–F-–SF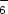 plasmas) are examined on the wave phase velocity and
the nonlinear localized pulse profile. The latter should satisfy necessary
condition to exist. The localized pulse of Ar+–F-–SF
plasmas) are examined on the wave phase velocity and
the nonlinear localized pulse profile. The latter should satisfy necessary
condition to exist. The localized pulse of Ar+–F-–SF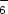 plasma is
much spiky than Xe+–F-–SF
plasma is
much spiky than Xe+–F-–SF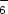 plasma. Thus, the mass ratio of the
negative-to-positive ions is focused upon and it emphasizes to play an
important role on the pulse profile. Dependence of the geometrical divergence
on the pulse profile is also investigated, which indicates that the localized
pulse damps with time. The implications of our results agrees with the
experimental observations.
plasma. Thus, the mass ratio of the
negative-to-positive ions is focused upon and it emphasizes to play an
important role on the pulse profile. Dependence of the geometrical divergence
on the pulse profile is also investigated, which indicates that the localized
pulse damps with time. The implications of our results agrees with the
experimental observations.
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2011




