https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2009-00189-2
Density functional study of the electronic structure and properties of lithium intercalated graphite
Physics Group, Birla Institute of Technology and Sciences, Pilani, 333031 Rajasthan, India
Corresponding authors: a rajuban@gmail.com bandy@bits-pilani.ac.in
Received:
17
March
2008
Revised:
12
November
2008
Published online:
30
June
2009
Ab initio electronic-structure
calculations are performed using density functional theory (DFT) with
polarized basis set (LanL2DZ and 6-311G++) within the spin polarized
generalized gradient approximation for lithium intercalated graphite.
Initially different benzene-Li+ model clusters are optimized on the
basis of their total energy at room temperature. These model clusters are
used to calculate the optimized structure of lithium intercalated graphite
clusters. The resultant optimized structures are used to calculate dipole
moment, ionization potential (IP), electron affinity (EA), binding energy
(BE) and vibrational spectra (IR and Raman). For an idea of the band gap
of the clusters in the ground state, the HOMO-LUMO gap (ΔEg
) has been calculated. To compare the electron transfer ability of
different clusters, chemical potential (μ), hardness (
η) and their ratio 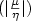 for different clusters have also been determined.
for different clusters have also been determined.
PACS: 31.15.E- – Density-functional theory / 32.10.Hq – Ionization potentials, electron affinities / 36.20.Ng – Vibrational and rotational structure, infrared and Raman spectra
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2009




