https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2005-00145-2
Studies of ion energy and yield from argon clusters heated by intense femtosecond laser pulses
1
Department of Physics, Shantou University, Shantou 515063, P.R. China
2
Laboratory for High Intensity Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine
Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, P.R. China
Corresponding author: a shli@stu.edu.cn
Received:
6
September
2004
Published online:
13
July
2005
Using time-of-flight spectrometry, the interaction of intense femtosecond
laser pulses with argon clusters has been studied by measuring the energy
and yield of emitted ions. With two different supersonic nozzles, the
dependence of average ion energy 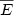 on cluster size
on cluster size 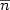 in a large range of
in a large range of 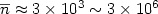 has been measured. The experimental results indicate that
when the cluster size
has been measured. The experimental results indicate that
when the cluster size 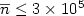 , the average ion
energy
, the average ion
energy 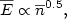 Coulomb explosion is the
dominant expansion mechanism. Beyond this size, the average ion energy gets
saturated gradually, the clusters exhibit a mixed Coulomb-hydrodynamic
expansion behavior. We also find that with the increasing gas backing
pressure, there is a maximum ion yield, the ion yield decreases as the gas
backing pressure is further increased.
Coulomb explosion is the
dominant expansion mechanism. Beyond this size, the average ion energy gets
saturated gradually, the clusters exhibit a mixed Coulomb-hydrodynamic
expansion behavior. We also find that with the increasing gas backing
pressure, there is a maximum ion yield, the ion yield decreases as the gas
backing pressure is further increased.
PACS: 36.40.Gk – Plasma and collective effects in clusters / 52.50.Jm – Plasma production and heating by laser beams (laser-foil, laser-cluster, etc.)
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2005




