https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2005-00121-x
The dissociation energy of V13+ and the consequences for radiative cooling
1
Department of Physics, Göteborg University, 41296 Göteborg,
Sweden
2
Institut für Physik,
Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-Universität Greifswald, Domstr. 10a, 17487
Greifswald, Germany
3
Institut für Physik, Johannes
Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, 55099 Mainz, Germany
4
Institut für Nukleare Entsorgung, Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe,
Postfach 3640, 76021 Karlsruhe, Germany
Corresponding author: a klavs@fy.chalmers.se
Received:
6
September
2004
Published online:
13
July
2005
The dissociation energy of V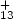 has been
determined by comparison of the rates of sequential fragmentation,
V
has been
determined by comparison of the rates of sequential fragmentation,
V , and
single-step fragmentation of the first fragment,
V
, and
single-step fragmentation of the first fragment,
V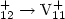 . The dissociation-energy value
obtained as D=4.35(13) eV has implications for the amount of
radiative cooling of the cluster derived form the data presented
earlier [C. Walther et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3816 (1999)]
and is used to analyze additional results.
. The dissociation-energy value
obtained as D=4.35(13) eV has implications for the amount of
radiative cooling of the cluster derived form the data presented
earlier [C. Walther et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3816 (1999)]
and is used to analyze additional results.
PACS: 36.40.Vz – Optical properties of clusters / 44.40.+a – Thermal radiation / 82.80.Ms – Mass spectrometry (including SIMS, multiphoton ionization and resonance ionization mass spectrometry, MALDI)
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2005




