https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2005-00037-5
Vibrational excitation and negative ion production in radio frequency parallel plate H2 plasmas
Dipartimento di Chimica dell'Universita' di Bari, Via Orabona 4, 70126
Bari, Italy
and
IMIP/CNR, Sez. Bari, Via Orabona 4, 70126 Bari, Italy
Corresponding author: a s.longo@chimica.uniba.it
Received:
16
December
2004
Published online:
12
April
2005
A theoretical study of the vibrational kinetics and attachment in low
pressure hydrogen plasmas produced by Radio Frequency (RF) discharges is
performed. In particular we study the influence of gas/surface kinetic
processes such as the vibrational deactivation and the atomic recombination
of molecules. The production of vibrationally excited molecules by the
surface recombination of atoms is also considered. The study is realized by
means of a self-consistent one dimensional kinetic model, and a parallel
plate RF discharge test case is implemented. Results show that surface
processes are
able to affect the vibrational distribution function
(vdf) and the negative ion (H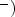 density. The effect of vibrational
exothermicity of H atom recombination is also discussed as a way to reduce
the gap between theory and experimental results. Moreover, it is shown that
the H- ion heating by the electric field strongly affects the
detachment rate: this effect is specially important for negative ions
produced through Rydberg states in this kind of discharges.
density. The effect of vibrational
exothermicity of H atom recombination is also discussed as a way to reduce
the gap between theory and experimental results. Moreover, it is shown that
the H- ion heating by the electric field strongly affects the
detachment rate: this effect is specially important for negative ions
produced through Rydberg states in this kind of discharges.
PACS: 52.20.-j – Elementary processes in plasmas / 52.65.-y – Plasma simulation / 52.50.Dg – Plasma sources
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2005




