https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2003-00129-2
Orbital magnetic moments and magnetic anisotropy energy in RhN and CoNPdM clusters
1
Instituto de Física, Universidad Autónoma de San Luis
Potosí, San Luis Potosí, Mexico
2
Laboratoire de Physique Quantique (UMR 5626 du CNRS) ,
Université Paul Sabatier, 31062 Toulouse Cedex, France
Corresponding author: a gustavo.pastor@irsamc.ups-tlse.fr
Received:
10
September
2002
Published online:
3
July
2003
The orbital magnetic moments 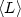 and the magnetic
anisotropy energy (MAE) of RhN (
and the magnetic
anisotropy energy (MAE) of RhN (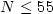 ) and Co19PdM
(M=24 and 60) are determined by using a self-consistent
real-space tight-binding method. For RhN,
) and Co19PdM
(M=24 and 60) are determined by using a self-consistent
real-space tight-binding method. For RhN, 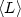 amounts typically 20–50% of the total magnetic moment
amounts typically 20–50% of the total magnetic moment
 +
+ 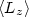 .
Strong oscillations as a function of N are observed with
a rapid convergence to zero as the spin magnetization vanishes
for
.
Strong oscillations as a function of N are observed with
a rapid convergence to zero as the spin magnetization vanishes
for  –50. In Co19PdM clusters, the magnetization
per Co atom is remarkably larger than in pure Co19.
This is mainly due to the local spin moments
–50. In Co19PdM clusters, the magnetization
per Co atom is remarkably larger than in pure Co19.
This is mainly due to the local spin moments 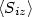 induced at the Pd atoms, which amount to about 20% of the spin
moment per Co atom
[
induced at the Pd atoms, which amount to about 20% of the spin
moment per Co atom
[ 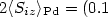 –
–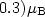 ] .
Large orbital moments are found at the Co atoms, particularly at the
Co/Pd interface. The anisotropy of
] .
Large orbital moments are found at the Co atoms, particularly at the
Co/Pd interface. The anisotropy of 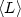 and the
associated MAE's are analyzed from a local perspective.
and the
associated MAE's are analyzed from a local perspective.
PACS: 36.40.Cg – Electronic and magnetic properties of clusters / 75.10.Lp – Band and itinerant models
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2003




