https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2003-00112-y
Temperature dependence of photoluminescence from mono-dispersed Si nanoparticles
1
Research Center for Advanced Manufacturing on Nanoscale Science and Engineering, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST),
1-2-1 Namiki, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8564, Japan
2
Institute of Materials Science, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8573, Japan
Corresponding author: a t.orii@aist.go.jp
Received:
10
September
2002
Published online:
3
July
2003
The temperature dependence of photoluminescence (PL) from mono-dispersed Si
nanoparticles was studied from 4 to 300 K. Si nanoparticles produced by pulsed laser ablation
in He background gas were sorted into the 6 nm size range by a differential mobility analyzer
(DMA). The spread of the size distribution was narrowed to a geometrical standard deviation 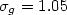 . On decreasing the temperature from 300 to 4 K, the intensity of the PL spectra
increased gradually, peaked at about 60 K, and then decreased rapidly. The temperature
dependences of the intensity and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) on the PL spectra
are discussed in terms of radiative and nonradiative decay rates.
. On decreasing the temperature from 300 to 4 K, the intensity of the PL spectra
increased gradually, peaked at about 60 K, and then decreased rapidly. The temperature
dependences of the intensity and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) on the PL spectra
are discussed in terms of radiative and nonradiative decay rates.
PACS: 61.46.+w – Nanoscale materials: clusters, nanoparticules, nanotubes, and nanocrystals / 78.55.Ap – Elemental semiconductors / 81.07.Bc – Nanocrystalline materials
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2003




