https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2002-00163-6
Vitamin E models
The effect of heteroatom substitution in 2-ethyl-2-methyl chroman and 2-ethyl-2-methyl-6-hydroxychroman
1
Global Institute of Computational Molecular and Materials Science VELOCET, 210 Dundas Street W., Suite 810, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5G 2E8
2
Department of Chemistry, University of Toronto, 80 St. George St.,
Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5S 3H6
3
Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy, Szeged University, Domter12, Szeged, Hungary-6701
4
Division of Cardiovascular Pharmacology,
Hungarian Academy of Sciences and
Szeged University, Domter12, Szeged, Hungary-6701
Corresponding authors: a dsetiadi@fixy.org - b gchass@fixy.org - c pyro@phcol.szote.u-szeged.hu - d varro@phcol.szote.u-szeged.hu - e papp@phcol.szote.u-szeged.hu - f icsizmad@alchemy.chem.utoronto.ca
Received:
9
May
2002
Revised:
9
July
2002
Published online:
13
September
2002
The molecular conformations of shortened molecular models of vitamin E (tocopherol
and tocotrienol) and their sulfur and selenium congeners were studied computationally at
the DFT level of theory [B3LYP/6-31G(d)]. The sequence of stabilization by the various heteroatoms was found to be the following: 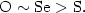 On the basis of the present structural results it seems that the seleno-congener of vitamin E is a distinct possibility.
On the basis of the present structural results it seems that the seleno-congener of vitamin E is a distinct possibility.
PACS: 31.15.Ar – Ab initio calculations
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2002




