https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e20020056
An analytic collisional-radiative model incorporating non-LTE and optical depth effects
Instituto de Física Arroyo Seco (IFAS),
Universidad Nacional del Centro Pinto 399, B7000GHG, Tandil and CONICET,
Argentina
Corresponding authors: a juanp@exa.unicen.edu.ar - b hdirocco@exa.unicen.edu.ar
Received:
12
June
2001
Revised:
24
October
2001
Published online: 15 April 2002
In this paper we analyze the variations in line intensities ratios due to a
non-equilibrium situation and to optical depth effects. A four level model
is proposed and the two particular situations for the possible transitions
are considered. Electron density and temperature as well as the source
thickness are used as independent parameters to find out in which way and
extent they modify the ratios of levels populations compared with the ideal
case of an equilibrium state and optically thin source. Accordingly with the
ion of interest, electron temperatures ranging from I/20 to I/7 eV (I
being the ionization energy), whereas electron densities in the interval
from 1014 to 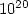 cm-3 will be considered. These ranges are
of special interest for diverse applications such as LIBS and measurement of
transition probabilities. Some results are presented for real ions and a new
expression for the escape factor is also proposed for general plasma
conditions.
cm-3 will be considered. These ranges are
of special interest for diverse applications such as LIBS and measurement of
transition probabilities. Some results are presented for real ions and a new
expression for the escape factor is also proposed for general plasma
conditions.
PACS: 52.25.-b – Plasma properties / 52.50.-b – Plasma production and heating / 52.70.-m – Plasma diagnostic techniques and instrumentation
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2002




