https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530170025
Formation of nitrogen-substituted carbon cluster anions by gas-feed Cs-sputtering from different forms of carbon
1
Nuclear Physics Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai 400085, India
2
Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science, Tata Institute of
Fundamental Research, Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400005, India
Corresponding authors: a anit@tifr.res.in - b pushan@tifr.res.in
Received:
30
May
2001
Revised:
17
August
2001
Published online: 15 November 2001
We have investigated the mechanism of formation of C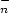 and CnN-
cluster anions during Cs+-ion sputtering from surfaces of different crystallographic
forms of carbon (polycrystalline graphite, amorphous C and C60), in the presence of
high purity N2 or NO2 gas. The normalised yields of sputter-ejected CnN- (
and CnN-
cluster anions during Cs+-ion sputtering from surfaces of different crystallographic
forms of carbon (polycrystalline graphite, amorphous C and C60), in the presence of
high purity N2 or NO2 gas. The normalised yields of sputter-ejected CnN- ( )
cluster anions display an oscillatory dependence on n: the odd n clusters being more
abundant than the even n ones. Significantly, CnN- clusters produced from the three
different forms of C, show similar oscillatory variations with n. Moreover, the CnN-
yields follow a single power law decline as a function of cluster size for all three
surfaces sputtered, and over a wide range of operating conditions. This strongly
indicates that the intrinsic structure of the ion-induced surface does not play a
significant role in the formation of sputtered cluster anions. The observed
abundance patterns of C
)
cluster anions display an oscillatory dependence on n: the odd n clusters being more
abundant than the even n ones. Significantly, CnN- clusters produced from the three
different forms of C, show similar oscillatory variations with n. Moreover, the CnN-
yields follow a single power law decline as a function of cluster size for all three
surfaces sputtered, and over a wide range of operating conditions. This strongly
indicates that the intrinsic structure of the ion-induced surface does not play a
significant role in the formation of sputtered cluster anions. The observed
abundance patterns of C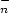 and CnN- clusters also suggest that mono-nitrogen
substitution of the carbon clusters does not allow the chain to ring transformation to
occur up to n = 10.
and CnN- clusters also suggest that mono-nitrogen
substitution of the carbon clusters does not allow the chain to ring transformation to
occur up to n = 10.
PACS: 36.40.Qv – Stability and fragmentation of clusters / 36.40.Wa – Charged clusters / 61.46.+w – Nanoscale materials: clusters, nanoparticles, nanotubes, and nanocrystals
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2001





