https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530070021
A collision-induced satellite in the Lyman β profile due to H-H collisions
Lyman β satellites
1
Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, Département Atomes et
Molécules en Astrophysique, 92195 Meudon Principal Cedex,
France
2
CNRS, Institut d'Astrophysique, 98bis boulevard Arago, 75014
Paris, France
3
Department of Physics, University of Louisville,
Louisville, Ky 40292, USA
4
Institut für Physikalische Chemie, Universität Heidelberg,
Im Neuenheimer Feld 229, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
Received:
15
January
2000
Revised:
17
May
2000
Published online: 15 November 2000
We present a theoretical profile of the
Lyman β line of atomic hydrogen perturbed by collisions
with neutral hydrogen atoms and protons.
We use a general unified theory in which the electric dipole moment
varies during a collision.
A collision-induced satellite appears on Lyman β, correlated to the
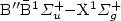 asymptotically forbidden transition of H2.
As a consequence,
the appearance of the
line wing between Lyman α and Lyman β is shown to be
sensitive to the relative abundance of hydrogen ions and neutral atoms,
and thereby to provide a temperature diagnostic for
stellar atmospheres and laboratory plasmas.
asymptotically forbidden transition of H2.
As a consequence,
the appearance of the
line wing between Lyman α and Lyman β is shown to be
sensitive to the relative abundance of hydrogen ions and neutral atoms,
and thereby to provide a temperature diagnostic for
stellar atmospheres and laboratory plasmas.
PACS: 32.70.Jz – Line shapes, widths, and shifts / 52.25.Qt – Emission, absorption, and scattering of ultraviolet radiation / 95.30.Dr – Atomic processes and interactions
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2000




