https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530050035
Evidence for N1/3 dependence of the sticking cross-section of atoms on small and medium-size van der Waals clusters
Laboratoire Collisions, Agrégats, Réactivité (UMR 5589 du CNRS) ,
IRSAMC, Université Paul Sabatier,
118 route de Narbonne,
31062 Toulouse Cedex 4, France
Corresponding author: a fcalvo@cea.fr
Received:
20
May
1999
Published online: 15 February 2000
This paper introduces a simple model describing the cluster growth
in supersonic
expansions. The predicted terminal mean cluster size is compared to the
available data in the case of argon. The agreement between the model and the
experimental results requires that the cross-section describing the sticking of
an atom on a cluster of size N scales like 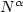 with α in the
range 0.34-0.44, well below the
with α in the
range 0.34-0.44, well below the  predicted by the simplest
geometrical scaling argument.
We explain this unexpected result in two steps. First, using Monte Carlo
simulations, we check that the potential between an atom and a cluster is
accurately represented by the Gspann and Vollmar potential, even at finite
temperature. Then, using
Langevin's approximation, we show that the sticking cross-section scales like
N1/3 for small to moderate N values and switches to the geometric scaling
predicted by the simplest
geometrical scaling argument.
We explain this unexpected result in two steps. First, using Monte Carlo
simulations, we check that the potential between an atom and a cluster is
accurately represented by the Gspann and Vollmar potential, even at finite
temperature. Then, using
Langevin's approximation, we show that the sticking cross-section scales like
N1/3 for small to moderate N values and switches to the geometric scaling
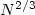 for very large N values. The crossover between these two scalings
occurs when
for very large N values. The crossover between these two scalings
occurs when 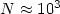 for argon, but the mean exponent α over the
size range 1-104 is 0.46. This N scaling of the sticking cross-section
should play an important role whenever condensation is important as it modifies
the kinetics of the early stages.
for argon, but the mean exponent α over the
size range 1-104 is 0.46. This N scaling of the sticking cross-section
should play an important role whenever condensation is important as it modifies
the kinetics of the early stages.
PACS: 34.50.-s – Scattering of atoms, molecules, and ions / 36.40.-c – Atomic and molecular clusters / 64.60.Qb – Nucleation
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 2000




