https://doi.org/10.1007/s100530050346
Atomic Rayleigh scattering cross-sections and the associated anomalous dispersion in the X-ray regions
1
Department of Physics, Sir. C.R.R. Autonomous College, C.R.R. Institutions, Eluru-534007,
W.G. Dt., A.P., India and The Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical
Physics, 34100 Trieste, Italy
2
Istituto di Matematica e Fisica, Università di Sassari, Via Vienna 2, 07100 Sassari, Italy
3
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma La Sapienza, P.le A. Moro 2, 00185 Roma, Italy
Received:
27
January
1998
Revised:
4
January
1999
Published online: 15 August 1999
Elastic scattering cross-sections for Pd, Ag, Cd, In, Sn, Sb, Pt, Au and
Pb are measured at an angle of 90° in the X-ray region 5.41 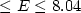 keV.
These energies fall between the high-energy side of the L- and M-shell absorption
edges of the atoms considered. The present atomic region is significant for
solid X-rays to assess the contribution of resonance and solid-state environmental
effects. Also it is the anomalous scattering region for many of the atoms
of the periodic table. Experimental results are compared with theoretical
calculations based on form factor formalisms including the anomalous corrections
and available recent S-matrix values. Based on the experimental evidence,
the present results indicate the influence of solid-state environmental effects,
the importance of anomalous corrections nearer to absorption edges, the correctness
of revised high-energy limit values, the superiority of S-matrix predictions
over form factor values on measured elastic scattering cross-sections in
the X-ray regime and also show the resonance behavior around K, L and M
absorption edges.
keV.
These energies fall between the high-energy side of the L- and M-shell absorption
edges of the atoms considered. The present atomic region is significant for
solid X-rays to assess the contribution of resonance and solid-state environmental
effects. Also it is the anomalous scattering region for many of the atoms
of the periodic table. Experimental results are compared with theoretical
calculations based on form factor formalisms including the anomalous corrections
and available recent S-matrix values. Based on the experimental evidence,
the present results indicate the influence of solid-state environmental effects,
the importance of anomalous corrections nearer to absorption edges, the correctness
of revised high-energy limit values, the superiority of S-matrix predictions
over form factor values on measured elastic scattering cross-sections in
the X-ray regime and also show the resonance behavior around K, L and M
absorption edges.
PACS: 78.70.-g – Interactions of particles and radiation with matter / 78.70.Ck – X-ray scattering / 61.10.Eq – X-ray scattering (including small-angle scattering)
© EDP Sciences, Società Italiana di Fisica, Springer-Verlag, 1999





