https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00720-7
Regular Article – Atomic Physics
The spectroscopic and transition properties of quadruply ionized bismuth: Bi V
Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University, 202002, Aligarh, India
Received:
6
May
2023
Accepted:
26
June
2023
Published online:
3
August
2023
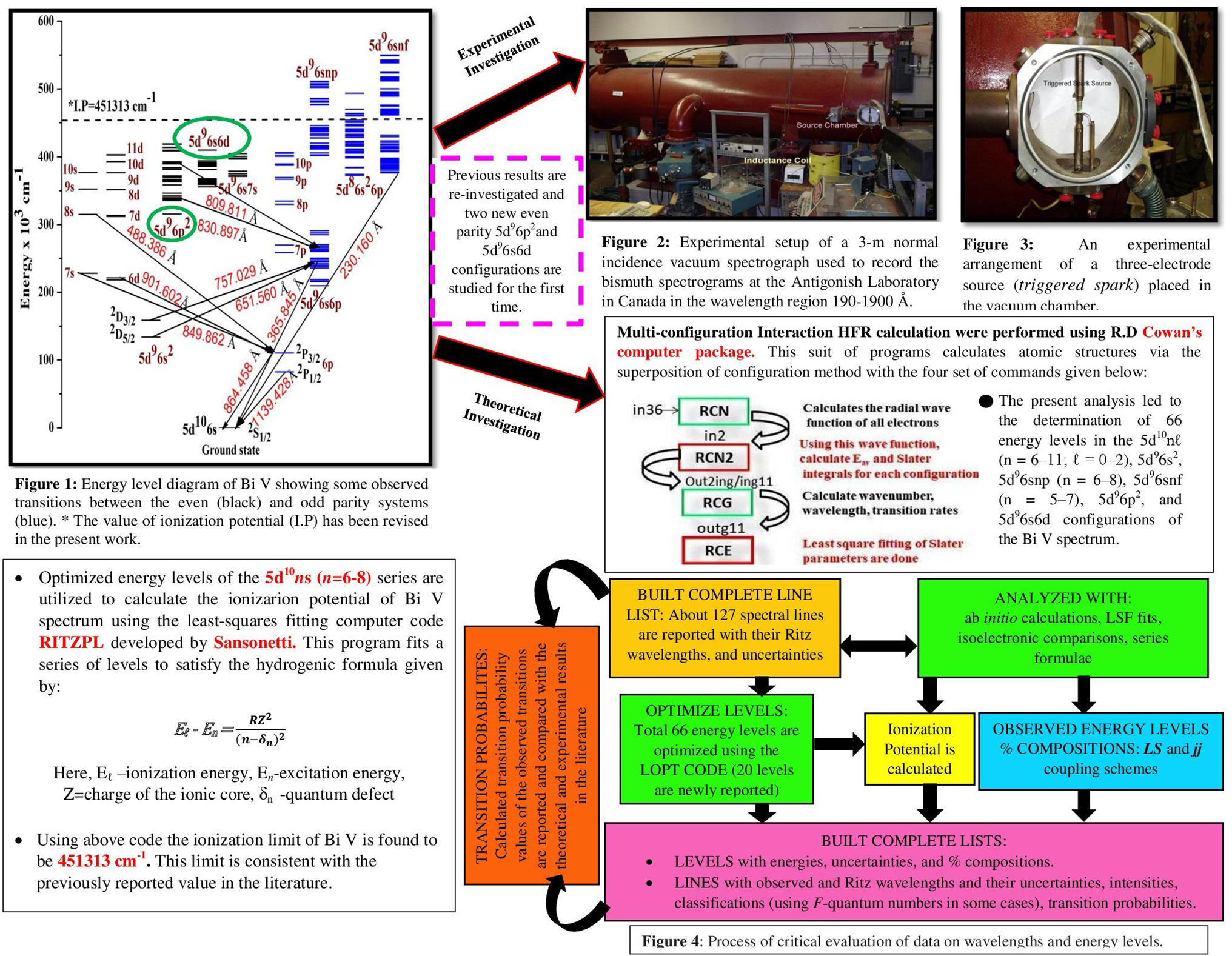
The spectrum of quadruply ionized bismuth (Bi V) has been investigated in the vacuum ultraviolet region 190–1900 Å. Several bismuth spectrograms were recorded on a 3-m Normal Incidence Spectrograph at the Antigonish laboratory in Canada using a triggered spark light source. The theoretical interpretation for this ion has been carried out by means of pseudo-relativistic Hartree–Fock approach implemented in the Cowan program. The previous results on the energy level structure of Bi V have been confirmed with the identification of five new energy levels of the partially studied configuration 5d96s6p. Fifteen energy levels affiliated to two new even parity configurations 5d96p2 and 5d96s6d were also established for the first time. The present analysis led to the determination of 66 energy levels in the 5d10nℓ (n = 6–11; ℓ = 0–2), 5d96s2, 5d96snp (n = 6–8), 5d96snf (n = 5–7), 5d96p2, and 5d96s6d configurations were optimized using the LOPT program. About 127 spectral lines identified in the Bi V spectrum are reported with their Ritz wavelengths and measurement uncertainties. The energy parameters were determined by least-squares fitting to the observed levels. Calculated transition probability values as well as LS and jj compositions obtained from fitted parameters are presented. A thorough comparison of the transition rates with previous theoretical and experimental results has been performed and the close agreement is observed. The ionization limit of Bi V is determined to be 451,313 cm−1.
The original online version of this article was revised: Table 2 was typeset incorrectly.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00747-w.
Copyright comment corrected publication 2023
Copyright comment Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023. corrected publication 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.