https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00362-1
Regular Article – Atomic and Molecular Collisions
Theoretical calculations of the photoionization cross sections for the ground and lowest two excited states of Ni XVIII ion
1
Department of Physics and Astrophysics, University of Delhi, 110007, Delhi, India
2
Department of Physics, Deen Dayal Upadhyaya College, University of Delhi, 110078, Delhi, India
3
Department of Physics, Kirori Mal College, University of Delhi, 110007, Delhi, India
4
School of Physical Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, 110067, Delhi, India
Received:
30
August
2021
Accepted:
7
February
2022
Published online:
28
March
2022
The Breit-Pauli R-matrix method in the close-coupling approximation is used for the calculation of total photoionization cross sections of the Ni XVIII ion in the ground state (2p63s2S1/2) and the lowest two excited states (2p63p2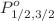 ). The core state wavefunctions are obtained from the configuration interaction technique (CIV3), and the energies of the Ni XIX residual ion are found to be in excellent agreement with the experimental values. It is observed that the present ionization potentials for the considered states are also in accordance with the experimental results. The fully relativistic Dirac atomic R-matrix calculations are performed for the photoionization cross sections of the ground state and the lowest two excited states to compare with our Breit-Pauli R-matrix results. Finally, the Quigley and Berrington method is adopted for investigating the autoionizing bound states arising from numerous open channels. The calculated photoionization cross sections are important for the determination of ionization balance, stellar plasma opacities, and spectral analysis.
). The core state wavefunctions are obtained from the configuration interaction technique (CIV3), and the energies of the Ni XIX residual ion are found to be in excellent agreement with the experimental values. It is observed that the present ionization potentials for the considered states are also in accordance with the experimental results. The fully relativistic Dirac atomic R-matrix calculations are performed for the photoionization cross sections of the ground state and the lowest two excited states to compare with our Breit-Pauli R-matrix results. Finally, the Quigley and Berrington method is adopted for investigating the autoionizing bound states arising from numerous open channels. The calculated photoionization cross sections are important for the determination of ionization balance, stellar plasma opacities, and spectral analysis.
The original online version of this article was revised to correct all equations on page 7.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-022-00405-7.
Copyright comment corrected publication 2022
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to EDP Sciences, SIF and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022. corrected publication 2022





